Renal Dysfunction and Tubulopathy Induced by High-Dose Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate in C57BL/6 Mice
- PMID: 33096887
- PMCID: PMC7711546
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare8040417
Renal Dysfunction and Tubulopathy Induced by High-Dose Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate in C57BL/6 Mice
Abstract
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) is the most preferred antiretroviral medicine in treating human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and hepatitis B virus (HBV) infections. Recent clinical trials have reported conflicting results on renal toxicity and safety in TDF-treated patients, but reference animal studies, testing high-doses of TDF for renal toxicity, are scarce. In this preclinical study, we investigated whether daily oral TDF administration (200, 500, or 800 mg/kg/d, p.o.) for four weeks induces renal insufficiency in C57BL/6 mice, by evaluating changes in body weight, urine micro-total protein, urinary microalbumin, serum blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and creatinine levels, along with histological examination of kidney samples. In the G3 group (TDF 800 mg/kg/d, p.o.), three mice died on the 17th, 23rd and 26th days, and overall, significant increases in urinary and serum levels were observed after two weeks of TDF treatment. In addition, the proportion of pyknotic epithelial cells and acidophilic cytoplasm in renal tubules was also increased after two weeks, and congestion and hemorrhage were observed in renal tubules after three weeks. Taken together, high-dose TDF treatment of 800 mg/kg/d might lead to renal tubular damage and dysfunction, great enough to cause death in mice, even after a short period of one to two weeks.
Keywords: nephrotoxicity; renal tubulopathy; tenofovir disoproxil fumarate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

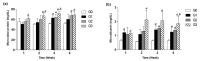


Similar articles
-
Recovery of Tenofovir-induced Nephrotoxicity following Switch from Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate to Tenofovir Alafenamide in Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Positive Patients.Infect Chemother. 2020 Sep;52(3):381-388. doi: 10.3947/ic.2020.52.3.381. Epub 2020 Jul 16. Infect Chemother. 2020. PMID: 32757496 Free PMC article.
-
Low Risk of Proximal Tubular Dysfunction Associated With Emtricitabine-Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate Preexposure Prophylaxis in Men and Women.J Infect Dis. 2016 Oct 1;214(7):1050-7. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw125. Epub 2016 Mar 29. J Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27029778 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Urinary β2 microglobulin can predict tenofovir disoproxil fumarate-related renal dysfunction in HIV-1-infected patients who initiate tenofovir disoproxil fumarate-containing antiretroviral therapy.AIDS. 2016 Jun 19;30(10):1563-71. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000001070. AIDS. 2016. PMID: 26919734
-
Altered Underlying Renal Tubular Function in Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B Receiving Nucleos(t)ide Analogs in a Real-World Setting: The MENTE Study.J Clin Gastroenterol. 2016 Oct;50(9):779-89. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000000569. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27332746
-
Drug safety evaluation of oral tenofovir disoproxil fumarate-emtricitabine for pre-exposure prophylaxis for human immunodeficiency virus infection.Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2016 Sep;15(9):1287-94. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2016.1211108. Epub 2016 Jul 25. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2016. PMID: 27391203 Review.
Cited by
-
Non-invasive Assessment of Subclinical Renal Parenchymal Changes in Chronic Hepatitis B Virus By T1 Mapping Magnetic Resonance Imaging.Balkan Med J. 2022 Mar 14;39(2):115-120. doi: 10.4274/balkanmedj.galenos.2021.2021-6-133. Balkan Med J. 2022. PMID: 35330558 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of drug-to-lipid ratio on nanodisc-based tenofovir drug delivery to the brain for HIV-1 infection.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2022 Jun;17(13):959-978. doi: 10.2217/nnm-2022-0043. Epub 2022 Jun 1. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2022. PMID: 35642549 Free PMC article.
-
Switching to besifovir in patients with chronic hepatitis B receiving tenofovir disoproxil fumarate: A randomized trial.Clin Mol Hepatol. 2025 Jul;31(3):810-822. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2024.0819. Epub 2025 Jan 17. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 39828249 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Metabolomics Study of Serum Samples of β-YAC Transgenic Mice Treated with Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 12;23(24):15750. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415750. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555396 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ristig M.B., Crippin J., Aberg J.A., Powderly W.G., Lisker-Melman M., Kessels L., Tebas P. Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate Therapy for Chronic Hepatitis B in Human Immunodeficiency Virus/Hepatitis B Virus–Coinfected Individuals for Whom Interferon-α and Lamivudine Therapy Have Failed. J. Infect. Dis. 2002;186:1844–1847. doi: 10.1086/345770. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nelson M.R., Katlama C., Montaner J.S., Cooper D.A., Gazzard B., Clotet B., Lazzarin A., Schewe K., Lange J., Wyatt C. The safety of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for the treatment of HIV infection in adults: The first 4 years. AIDS. 2007;21:1273–1281. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e3280b07b33. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

