Defining the Functional Targets of Cap'n'collar Transcription Factors NRF1, NRF2, and NRF3
- PMID: 33096892
- PMCID: PMC7588902
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox9101025
Defining the Functional Targets of Cap'n'collar Transcription Factors NRF1, NRF2, and NRF3
Abstract
The NRF transcription factors NRF1, NRF2, and NRF3, are a subset of Cap'n'collar transcriptional regulators which modulate the expression of genes harboring antioxidant-response element (ARE) sequences within their genomic loci. Despite the emerging physiological importance of NRF family members, the repertoire of their genetic targets remains incompletely defined. Here we use RNA-sequencing-based transcriptional profiling and quantitative proteomics to delineate the overlapping and differential genetic programs effected by the three NRF transcription factors. We then create consensus target gene sets regulated by NRF1, NRF2, and NRF3 and define the integrity of these gene sets for probing NRF activity in mammalian cell culture and human tissues. Together, our data provide a quantitative assessment of how NRF family members sculpt proteomes and transcriptomes, providing a framework to understand the critical physiological importance of NRF transcription factors and to establish pharmacologic approaches for therapeutically activating these transcriptional programs in disease.
Keywords: NRF transcription factors; cellular pathway analysis; oxidative stress response; proteomics; transcriptomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



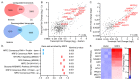

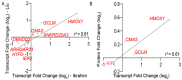
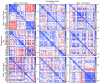
References
-
- Shivdasani R.A., Rosenblatt M.F., Zucker-Franklin D., Jackson C.W., Hunt P., Saris C.J., Orkin S.H. Transcription factor NF-E2 is required for platelet formation independent of the actions of thrombopoietin/MGDF in megakaryocyte development. Cell. 1995;81:695–704. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90531-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Itoh K., Chiba T., Takahashi S., Ishii T., Igarashi K., Katoh Y., Oyake T., Hayashi N., Satoh K., Hatayama I., et al. An Nrf2/small Maf heterodimer mediates the induction of phase II detoxifying enzyme genes through antioxidant response elements. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997;236:313–322. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1997.6943. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Celentano S., Capolongo G., Pollastro R.M. Bardoxolone: A new potential therapeutic agent in the treatment of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease? Giornale Italiano di Nefrologia. 2019;36:2019-vol5. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

