Use of Biodegradable, Chitosan-Based Nanoparticles in the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 33096898
- PMCID: PMC7587961
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25204866
Use of Biodegradable, Chitosan-Based Nanoparticles in the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
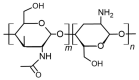
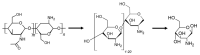
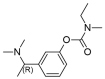
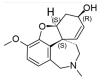
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that affects more than 24 million people worldwide and represents an immense medical, social and economic burden. While a vast array of active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) is available for the prevention and possibly treatment of AD, applicability is limited by the selective nature of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) as well as by their severe peripheral side effects. A promising solution to these problems is the incorporation of anti-Alzheimer drugs in polymeric nanoparticles (NPs). However, while several polymeric NPs are nontoxic and biocompatible, many of them are not biodegradable and thus not appropriate for CNS-targeting. Among polymeric nanocarriers, chitosan-based NPs emerge as biodegradable yet stable vehicles for the delivery of CNS medications. Furthermore, due to their mucoadhesive character and intrinsic bioactivity, chitosan NPs can not only promote brain penetration of drugs via the olfactory route, but also act as anti-Alzheimer therapeutics themselves. Here we review how chitosan-based NPs could be used to address current challenges in the treatment of AD; with a specific focus on the enhancement of blood-brain barrier penetration of anti-Alzheimer drugs and on the reduction of their peripheral side effects.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; CNS delivery; amyloid-β; biodegradable; blood-brain barrier; chitosan; polymer nanoparticle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chitosan as a suitable nanocarrier material for anti-Alzheimer drug delivery.Int J Biol Macromol. 2015 Jan;72:454-65. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.08.052. Epub 2014 Sep 6. Int J Biol Macromol. 2015. PMID: 25199867 Review.
-
Development, optimisation and evaluation of chitosan nanoparticles of alendronate against Alzheimer's disease in intracerebroventricular streptozotocin model for brain delivery.J Drug Target. 2021 Feb;29(2):199-216. doi: 10.1080/1061186X.2020.1817041. Epub 2020 Sep 10. J Drug Target. 2021. PMID: 32876502
-
Chrysin-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticle-Mediated Neuroprotection in Aβ1-42-Induced Neurodegenerative Conditions in Zebrafish.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2022 Jul 6;13(13):2017-2034. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.2c00240. Epub 2022 Jun 13. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35696319
-
Intranasal delivery of Huperzine A to the brain using lactoferrin-conjugated N-trimethylated chitosan surface-modified PLGA nanoparticles for treatment of Alzheimer's disease.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Feb 1;13:705-718. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S151474. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 29440896 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctional Nanocarriers for Alzheimer's Disease: Befriending the Barriers.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 May;61(5):3042-3089. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03730-z. Epub 2023 Nov 15. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 37966683 Review.
Cited by
-
Marine-derived Compounds: A Powerful Platform for the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease.Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2024;24(2):166-181. doi: 10.2174/0118715249269050231129103002. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38305396 Review.
-
Potential Applications of Natural Components of Traditional Chinese Medicine Delivery via Nanoparticle Drug Delivery Systems in the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Jun 17;20:7781-7810. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S525960. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40546798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel fabrication of Cu(II)-incorporated chiral d-penicillamine-chitosan nanocomposites enantio-selectively inhibit the induced amyloid β aggregation for Alzheimer's disease therapy.Heliyon. 2023 Dec 11;10(1):e23563. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23563. eCollection 2024 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38223723 Free PMC article.
-
Chitosan-based nanoparticles in Alzheimer's disease: messenger or message?Neural Regen Res. 2021 Nov;16(11):2204-2205. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.310685. Neural Regen Res. 2021. PMID: 33818494 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Photobiomodulation in Alzheimer's Disease-A Complementary Method to State-of-the-Art Pharmaceutical Formulations and Nanomedicine?Pharmaceutics. 2023 Mar 11;15(3):916. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15030916. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36986776 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
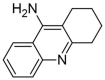
- Tamilselvan N., Raghavan C.V. Formulation and characterization of anti-alzheimer’s drug loaded chitosan nanoparticles and its In vitro biological evaluation. J. Young Pharm. 2015;7:28–35. doi: 10.5530/jyp.2015.1.6. - DOI
-
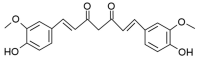
- Hassanzadeh G., Fallahi Z., Khanmohammadi M., Elmizadeh H. Effect of Magnetic Tacrine-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles on Spatial Learning, Memory, Amyloid Precursor Protein and Seladin-1 Expression in the Hippocampus of Streptozotocin-Exposed Rats. Int. Clin. Neurosci. J. 2016;3:25–31. doi: 10.22037/icnj.v3i1.12358. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

