Prognostic value of preoperative lymphocyte-related systemic inflammatory biomarkers in upper tract urothelial carcinoma patients treated with radical nephroureterectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 33097052
- PMCID: PMC7585317
- DOI: 10.1186/s12957-020-02048-7
Prognostic value of preoperative lymphocyte-related systemic inflammatory biomarkers in upper tract urothelial carcinoma patients treated with radical nephroureterectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Growing evidence shows that the preoperative lymphocyte-related systemic inflammatory biomarkers are associated with the prognosis of patients with upper tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC). These markers include neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), and monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio (MLR). However, these findings are inconsistent, and the prognostic significance of these biomarkers is unclear. Moreover, the currently available prognostic indicators do not precisely predict the outcome of UTUC patients. This motivated us to investigate the prognostic values of NLR, PLR, and MLR in UTUC patients treated with radical nephroureterectomy (RNU).
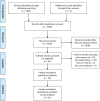
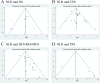
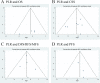
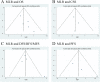
Methods: We prospectively registered this in PROSPERO (CRD42020186531). We performed a comprehensive literature search of the PubMed, Web of Science, EMBASE, and Cochrane Library databases to identify the eligible studies evaluating the prognostic values of preoperative NLR, PLR, and MLR. Hazard ratios with 95% confidence intervals of overall survival (OS), cancer-specific survival (CSS), disease-free survival (DFS), recurrence-free survival (RFS), metastasis-free survival (MFS), and progression-free survival (PFS) were extracted from the multivariate analyses and analyzed with fixed or random effects models when applicable. Heterogeneity among the studies was evaluated using Cochran's Q test and I2 statistic. Sensitivity and subgroup analyses were conducted to explore the origin of heterogeneity. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) was applied to assess the quality of each enrolled study. Publication bias was determined using funnel plots together with Egger's tests. The Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) was used to evaluate the quality of the evidence.
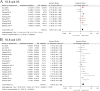
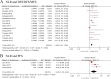
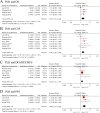
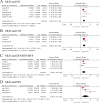
Results: Overall, we included 10,339 UTUC patients from twenty-five retrospective studies. The results indicated that elevated preoperative NLR, PLR, and MLR were significantly associated with worse OS, CSS, DFS/RFS/MFS, and PFS in the UTUC patients undergoing RNU. Furthermore, the results of sensitivity and subgroup analyses demonstrated the rationality and reliability of the results.
Conclusions: The present meta-analysis demonstrated a significant association between elevated preoperative NLR, PLR, and MLR and poor prognosis in patients with surgically treated UTUC. Hence, lymphocyte-related systemic inflammatory biomarkers, in conjunction with clinicopathological factors, molecular markers, and other prognostic indicators, could be helpful to determine the primary treatment strategies and to design individualized follow-up plans for UTUC patients.
Keywords: Biomarker; Meta-analysis; Monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio; Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio; Prognosis; Upper tract urothelial carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

