All Treatment Parameters Affect Environmental Surface Sanitation Efficacy, but Their Relative Importance Depends on the Microbial Target
- PMID: 33097504
- PMCID: PMC7755260
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01748-20
All Treatment Parameters Affect Environmental Surface Sanitation Efficacy, but Their Relative Importance Depends on the Microbial Target
Abstract
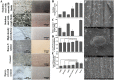
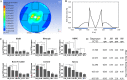
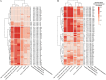
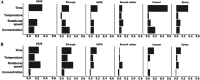
Environmental sanitation in food manufacturing plants promotes food safety and product microbial quality. However, the development of experimental models remains a challenge due to the complex nature of commercial cleaning processes, which include spraying water and sanitizer on equipment and structural surfaces within manufacturing space. Although simple in execution, the physical driving forces are difficult to simulate in a controlled laboratory environment. Here, we present a bench-scale bioreactor system which mimics the flow conditions in environmental sanitation programs. We applied computational fluid dynamic (CFD) simulations to obtain fluid flow parameters that better approximate and predict industrial outcomes. According to the CFD model, the local wall shear stress achieved on the target surface ranged from 0.015 to 5.00 Pa. Sanitation efficacy on six types of environmental surface materials (hydrophobicity, 57.59 to 88.61°; roughness, 2.2 to 11.9 μm) against two different microbial targets, the bacterial pathogen Listeria monocytogenes and Exophiala species spoilage fungi, were evaluated using the bench-scale bioreactor system. The relative reduction ranged from 0.0 to 0.82 for Exophiala spp., which corresponded to a 0.0 to 2.21 log CFU/coupon reduction, and the relative reduction ranged from 0.0 to 0.93 in L. monocytogenes which corresponded to a 0.0 to 6.19 log CFU/coupon reduction. Although most treatment parameters were considered statistically significant against either L. monocytogenes or Exophiala spp., contact time was ranked as the most important predictor for L. monocytogenes reduction. Shear stress contributed the most to Exophiala spp. removal on stainless steel and Buna-N rubber, while contact time was the most important factor on HDPE (high-density polyethylene), cement, and epoxy.IMPORTANCE Commercial food manufacturers commonly employ a single sanitation program that addresses both bacterial pathogen and fungal spoilage microbiota, despite the fact that the two microbial targets respond differently to various environmental sanitation conditions. Comparison of outcome-based clusters of treatment combinations may facilitate the development of compensatory sanitation regimes where longer contact time or greater force are applied so that lower sanitizer concentrations can be used. Determination of microbiological outcomes related to sanitation program efficacy against a panel of treatment conditions allows food processors to balance tradeoffs between quality and safety with cost and waste stream management, as appropriate for their facility.
Keywords: computational fluid dynamics; food safety; sanitation; spoilage.
Copyright © 2020 Cai et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of cleaning and sanitation methods against Listeria innocua on apple packing equipment surfaces.Food Microbiol. 2022 Oct;107:104061. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2022.104061. Epub 2022 May 19. Food Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35953171
-
Behavior of Listeria monocytogenes in a multi-species biofilm with Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium and control through sanitation procedures.Int J Food Microbiol. 2015 May 4;200:5-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2015.01.003. Epub 2015 Jan 22. Int J Food Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25655573
-
Comparison of flow characteristics in a bench-scale system with commercial-scale pipelines: Use of computational fluid dynamics (CFD).J Food Sci. 2021 Jul;86(7):3097-3108. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.15814. Epub 2021 Jun 23. J Food Sci. 2021. PMID: 34160072
-
Upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor--a review.Indian J Environ Health. 2001 Apr;43(2):1-82. Indian J Environ Health. 2001. PMID: 12397675 Review.
-
Identification and classification of sampling sites for pathogen environmental monitoring programs for Listeria monocytogenes: Results from an expert elicitation.Food Microbiol. 2018 Oct;75:2-17. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2017.07.005. Epub 2017 Jul 11. Food Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30056959
Cited by
-
A simulation model to quantify the efficacy of dry cleaning interventions on a contaminated milk powder line.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025 May 21;91(5):e0208624. doi: 10.1128/aem.02086-24. Epub 2025 Apr 17. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40243318 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic characterization of polyextremotolerant black yeasts isolated from food and food production environments.Front Fungal Biol. 2022 Jul 26;3:928622. doi: 10.3389/ffunb.2022.928622. eCollection 2022. Front Fungal Biol. 2022. PMID: 37746166 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial food spoilage: impact, causative agents and control strategies.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2024 Sep;22(9):528-542. doi: 10.1038/s41579-024-01037-x. Epub 2024 Apr 3. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38570695 Review.
-
Genomic analysis of Listeria monocytogenes from US food processing environments reveals a high prevalence of QAC efflux genes but limited evidence of their contribution to environmental persistence.BMC Genomics. 2022 Jul 4;23(1):488. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08695-2. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35787787 Free PMC article.
-
Survival of Escherichia coli O157:H7 during Moderate Temperature Dehydration of Plant-Based Foods.Foods. 2021 Sep 13;10(9):2162. doi: 10.3390/foods10092162. Foods. 2021. PMID: 34574271 Free PMC article.
References
-
- U.S. FDA. 2017. Draft guidance for industry: control of Listeria monocytogenes in ready-to-eat foods. Fed Regist 82:4803–4805.
-
- Goode KR, Phinney D, Hasting T, Fryer P. 2018. Engineering considerations for cleaning and disinfection in the food industry, p 1125–1174. In Handbook of food engineering. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
