T cell regeneration after immunological injury
- PMID: 33097917
- PMCID: PMC7583557
- DOI: 10.1038/s41577-020-00457-z
T cell regeneration after immunological injury
Abstract
Following periods of haematopoietic cell stress, such as after chemotherapy, radiotherapy, infection and transplantation, patient outcomes are linked to the degree of immune reconstitution, specifically of T cells. Delayed or defective recovery of the T cell pool has significant clinical consequences, including prolonged immunosuppression, poor vaccine responses and increased risks of infections and malignancies. Thus, strategies that restore thymic function and enhance T cell reconstitution can provide considerable benefit to individuals whose immune system has been decimated in various settings. In this Review, we focus on the causes and consequences of impaired adaptive immunity and discuss therapeutic strategies that can recover immune function, with a particular emphasis on approaches that can promote a diverse repertoire of T cells through de novo T cell formation.
Conflict of interest statement
M.R.M.v.d.B. has received research support and stock options from Seres Therapeutics, has received royalties from Wolters Kluwer, has consulted for, received honoraria from or participated in advisory boards for Seres Therapeutics, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Rheos, Therakos, WindMIL Therapeutics, Amgen, Merck & Co. Inc., Magenta Therapeutics, DKMS Medical Council (board), Forty Seven Inc. (spouse), Pharmacyclics (spouse) and Kite Pharmaceuticals (spouse) and has intellectual property licensing agreements with Seres Therapeutics and Juno Therapeutics. E.V. has acted as a consultant for and received honoraria from Ferring Pharmaceuticals. M.R.M.v.d.B. is an inventor on a patent application (US2015/058095) submitted by Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. Two provisional patent applications have been filed (US 15/033,178 and US 62/566,897) with E.V. and M.R.M.v.d.B. listed as inventors. J.J.T. declares no competing interests.
Figures

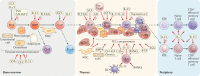
References
-
- Nikolich-Žugich J, Slifka MK, Messaoudi I. The many important facets of T-cell repertoire diversity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004;4:123–132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

