Brain arteriolosclerosis
- PMID: 33098484
- PMCID: PMC8503820
- DOI: 10.1007/s00401-020-02235-6
Brain arteriolosclerosis
Abstract
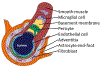
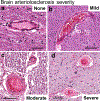
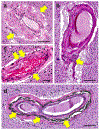
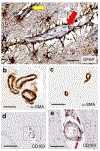
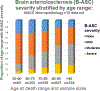
Brain arteriolosclerosis (B-ASC), characterized by pathologic arteriolar wall thickening, is a common finding at autopsy in aged persons and is associated with cognitive impairment. Hypertension and diabetes are widely recognized as risk factors for B-ASC. Recent research indicates other and more complex risk factors and pathogenetic mechanisms. Here, we describe aspects of the unique architecture of brain arterioles, histomorphologic features of B-ASC, relevant neuroimaging findings, epidemiology and association with aging, established genetic risk factors, and the co-occurrence of B-ASC with other neuropathologic conditions such as Alzheimer's disease and limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy (LATE). There may also be complex physiologic interactions between metabolic syndrome (e.g., hypertension and inflammation) and brain arteriolar pathology. Although there is no universally applied diagnostic methodology, several classification schemes and neuroimaging techniques are used to diagnose and categorize cerebral small vessel disease pathologies that include B-ASC, microinfarcts, microbleeds, lacunar infarcts, and cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA). In clinical-pathologic studies that factored in comorbid diseases, B-ASC was independently associated with impairments of global cognition, episodic memory, working memory, and perceptual speed, and has been linked to autonomic dysfunction and motor symptoms including parkinsonism. We conclude by discussing critical knowledge gaps related to B-ASC and suggest that there are probably subcategories of B-ASC that differ in pathogenesis. Observed in over 80% of autopsied individuals beyond 80 years of age, B-ASC is a complex and under-studied contributor to neurologic disability.
Keywords: Arteriosclerosis; Neuroimaging; Neuropathology; SVD; Senescence; cAVU.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P50 AG047266/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005138/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG047366/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010129/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG019610/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG061551/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K24AG053435/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013854/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG053760/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AG057461/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG057191/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062428/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010124/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG023501/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072946/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG039621/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 NS100717/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- G1100540/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P50 AG005142/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG061111/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG055449/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005146/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG072122/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AG053435/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG028383/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062421/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG035982/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG008702/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 NS118584/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD064993/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U54 NS100717/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG057191/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG016976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG008051/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013846/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG047270/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062429/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005136/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG049638/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG012300/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G0900652/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P30 AG062422/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016573/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G0502157/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P30 AG008017/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG025688/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG016976/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- G0400074/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AG055449/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG039621/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG057187/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD023573/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD064993/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG028383/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG039621/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG057187/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- TL1 TR001997/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

