Derivation of Airway Basal Stem Cells from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells
- PMID: 33098807
- PMCID: PMC7796997
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2020.09.017
Derivation of Airway Basal Stem Cells from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells
Abstract
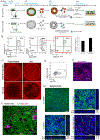
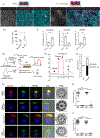
The derivation of tissue-specific stem cells from human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) would have broad reaching implications for regenerative medicine. Here, we report the directed differentiation of human iPSCs into airway basal cells ("iBCs"), a population resembling the stem cell of the airway epithelium. Using a dual fluorescent reporter system (NKX2-1GFP;TP63tdTomato), we track and purify these cells as they first emerge as developmentally immature NKX2-1GFP+ lung progenitors and subsequently augment a TP63 program during proximal airway epithelial patterning. In response to primary basal cell medium, NKX2-1GFP+/TP63tdTomato+ cells display the molecular and functional phenotype of airway basal cells, including the capacity to self-renew or undergo multi-lineage differentiation in vitro and in tracheal xenografts in vivo. iBCs and their differentiated progeny model perturbations that characterize acquired and genetic airway diseases, including the mucus metaplasia of asthma, chloride channel dysfunction of cystic fibrosis, and ciliary defects of primary ciliary dyskinesia.
Keywords: airway regeneration; basal cells; directed differentiation; induced pluripotent stem cells.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
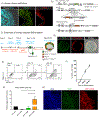

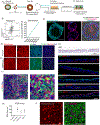
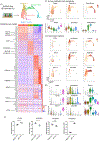
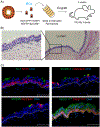
References
-
- Carraro G, Langerman J, Sabri S, Lorenzana Z, Purkayastha A, Konda B, Aros CJ, Calvert BA, Szymaniak A, Wilson E, et al. (2020a). A molecular atlas of proximal airway identifies subsets of known airway cell types revealing details of the unique molecular pathogenesis of Cystic Fibrosis. 499, 1–23.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 HL119215/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K12 HD052896/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL146601/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007035/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL134745/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL139799/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 DK110805/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL095993/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL122442/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 TR001810/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK072482/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL134766/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL148692/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020C00005/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL139876/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK065988/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001430/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL128370/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

