Avatar identification and problematic gaming: The role of self-concept clarity
- PMID: 33099249
- PMCID: PMC7539898
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2020.106694
Avatar identification and problematic gaming: The role of self-concept clarity
Abstract
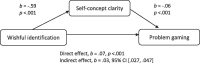
Some video-gaming activities feature customizable avatars that enable users to fulfil self-identity needs. Research evidence (e.g., fMRI and survey studies) has suggested that poorer self-concept and stronger avatar identification are associated with problematic gaming. Player-avatar relationships have thus been proposed to require attention in gaming disorder assessment and interventions. To examine the interplay of player-avatar interactions in problematic gaming, this study investigated whether avatar identification differed according to avatar characteristics and game types, and whether the association between avatar identification and problem gaming was mediated by self-concept clarity. A total of 993 adult respondents completed an online survey that assessed problematic gaming, avatar identification, and self-concept clarity. The results indicated that avatar identification scores were generally unrelated to avatar characteristics (e.g., human resemblance, degree of customizability, and in-game perspective). Avatar identification was significantly positively related to problematic gaming and significantly negatively related to self-concept clarity. There was a significant indirect relationship between avatar identification on problem gaming mediated through self-concept clarity. These findings suggest that poorer self-concept clarity may be one mechanism by which avatar identification affects problem gaming. Future research with clinical samples may help to gain a better understanding of avatar-related processes and psychological vulnerabilities related to problematic gaming.
Keywords: Avatar identification; Gaming disorder; Problematic gaming; Self-concept clarity.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Player-avatar interactions in habitual and problematic gaming: A qualitative investigation.J Behav Addict. 2021 Jul 8;10(2):223-233. doi: 10.1556/2006.2021.00038. J Behav Addict. 2021. PMID: 34280128 Free PMC article.
-
Avatar- and self-related processes and problematic gaming: A systematic review.Addict Behav. 2020 Sep;108:106461. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2020.106461. Epub 2020 May 8. Addict Behav. 2020. PMID: 32480244
-
Exploring the Neural Basis of Avatar Identification in Pathological Internet Gamers and of Self-Reflection in Pathological Social Network Users.J Behav Addict. 2016 Sep;5(3):485-99. doi: 10.1556/2006.5.2016.048. Epub 2016 Jul 14. J Behav Addict. 2016. PMID: 27415603 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Avatar Identification on the Attraction of Virtual Reality Games: Survey Study.JMIR Form Res. 2024 Oct 22;8:e56704. doi: 10.2196/56704. JMIR Form Res. 2024. PMID: 39437383 Free PMC article.
-
Maladaptive player-game relationships in problematic gaming and gaming disorder: A systematic review.Clin Psychol Rev. 2019 Nov;73:101777. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2019.101777. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Clin Psychol Rev. 2019. PMID: 31707185
Cited by
-
Deep learning(s) in gaming disorder through the user-avatar bond: A longitudinal study using machine learning.J Behav Addict. 2023 Nov 9;12(4):878-894. doi: 10.1556/2006.2023.00062. Print 2023 Dec 22. J Behav Addict. 2023. PMID: 37943343 Free PMC article.
-
Player-avatar interactions in habitual and problematic gaming: A qualitative investigation.J Behav Addict. 2021 Jul 8;10(2):223-233. doi: 10.1556/2006.2021.00038. J Behav Addict. 2021. PMID: 34280128 Free PMC article.
-
User-avatar bond as diagnostic indicator for gaming disorder: A word on the side of caution.J Behav Addict. 2024 Nov 22;13(4):885-893. doi: 10.1556/2006.2024.00032. Print 2024 Dec 30. J Behav Addict. 2024. PMID: 39576292 Free PMC article.
-
[Indicators of abusive use of video games in adolescents aged 12 to 14 years. Assessment by a panel of experts].Aten Primaria. 2025 Apr 21;57(10):103255. doi: 10.1016/j.aprim.2025.103255. Online ahead of print. Aten Primaria. 2025. PMID: 40262263 Free PMC article. Spanish.
-
Exploring e-sports fans' motivation for watching live streams based on self-determination theory.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 15;14(1):13858. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-64712-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38879690 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allison S.E., Von Wahlde L., Shockley T., Gabbard G.O. The development of the self in the era of the internet and role-playing fantasy games. American Journal of Psychiatry. 2006;163:381–385. - PubMed
-
- Bean A.M., Nielsen R.K., van Rooij A.J., Ferguson C.J. Video game addiction: The push to pathologize video games. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice. 2017;48(5):378.
-
- Bessière K., Seay A.F., Kiesler S. The ideal elf: Identity exploration in World of Warcraft. Cyberpsychology & Behavior. 2007;10:530–535. - PubMed
-
- Billieux J., Thorens G., Khazaal Y., Zullino D., Achab S., Van der Linden M. Problematic involvement in online games: A cluster analytic approach. Computers in Human Behavior. 2015;43:242–250.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

