nal-IRI+5-FU/LV versus 5-FU/LV in post-gemcitabine metastatic pancreatic cancer: Randomized phase 2 trial in Japanese patients
- PMID: 33099898
- PMCID: PMC7774735
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.3558
nal-IRI+5-FU/LV versus 5-FU/LV in post-gemcitabine metastatic pancreatic cancer: Randomized phase 2 trial in Japanese patients
Abstract
Background: In the NAPOLI-1 phase 3 trial, liposomal irinotecan (nal-IRI) +5-fluorouracil/leucovorin (5-FU/LV) significantly increased mPFS versus 5-FU/LV (3.1 vs. 1.5 months [unstratified HR = 0.56, p = 0.0001]) in patients with mPAC that progressed on prior gemcitabine-based therapy. This randomized phase 2 trial evaluated nal-IRI+5-FU/LV tolerability (Part 1), safety, and efficacy (Part 2; outcomes reported here) in Japanese patients with mPAC that progressed on gemcitabine-based therapy.
Methods: Patients were randomized 1:1 and stratified by KPS (70 and 80 vs. ≥90) and baseline albumin (≥4.0 g/dl vs. <4.0 g/dl). Primary endpoint was PFS; secondary endpoints were ORR, DCR, OS, TTF, CA19-9 response, and QoL. The ITT population comprised all randomized patients.
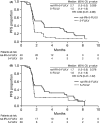
Results: Patient characteristics differed between nal-IRI+5-FU/LV (n = 40) and 5-FU/LV (n = 39) arms, including baseline hepatic lesions (63% vs. 51%), stage IV disease at diagnosis (78% vs. 51%), and post-study anticancer therapy (55% vs. 72%). Investigator-assessed mPFS increase with nal-IRI+5-FU/LV was clinically meaningful and statistically significant versus 5-FU/LV (2.7 vs. 1.5 months, HR = 0.60). Independently assessed mPFS showed similar trends (1.7 vs. 1.6 months, HR = 0.79). mOS was 6.3 months with nal-IRI+5-FU/LV and not reached with 5-FU/LV. ORR increased significantly with nal-IRI+5-FU/LV versus 5-FU/LV (18% vs. 0, rate difference 17.5). Commonly reported grade ≥3 treatment-emergent AEs were decreased neutrophil count (37% vs. 3%), decreased white blood cell count (20% vs. 0), and diarrhea (17% vs. 3%).
Conclusions: In conclusion, clinically meaningful and statistically significant gains in investigator-assessed PFS and ORR were observed with nal-IRI+5-FU/LV versus 5-FU/LV in Japanese patients, with no new or unexpected safety signals. (Clinicaltrials.gov ID: NCT02697058).
Keywords: chemotherapy; clinical trials; medical oncology; pancreatic cancer; pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
© 2020 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Ferlay J, Ervik M, Lam F, et al. Global cancer observatory: cancer today. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2018. https://gco.iarc.fr/today
-
- Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe: estimates for 40 countries and 25 major cancers in 2018. Eur J Cancer. 2018;103:356–387. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69:7–34. - PubMed
-
- Rahib L, Smith BD, Aizenberg R, Rosenzweig AB, Fleshman JM, Matrisian LM. Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res. 2014;74:2913–2921. - PubMed
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

