Factors predicting loss of cervical lordosis following cervical laminoplasty: A critical review
- PMID: 33100764
- PMCID: PMC7546055
- DOI: 10.4103/jcvjs.JCVJS_70_20
Factors predicting loss of cervical lordosis following cervical laminoplasty: A critical review
Abstract
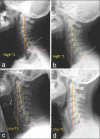
Background: Laminoplasty is a method of posterior cervical decompression which indirectly decompresses the spinal column. Unfortunately, many patients undergoing laminoplasty develops postoperative loss of cervical lordosis (LCL) or kyphotic alignment of cervical spine even though they have sufficient preoperative lordosis which results in poor surgical outcome.
Objective: We would like to highlight the relationship between various radiological parameters of cervical alignment and postoperative LCL in patients undergoing laminoplasty.
Methods: We performed extensive literature search using PubMed, Google Scholar, and Web of Science for relevant articles that report factors affecting cervical alignment following laminoplasty.
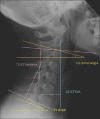
Results: On reviewing the literature, patients with high T1 slope have more lordotic alignment of cervical spine preoperatively. They also have more chances of LCL following laminoplasty. C2-C7 sagittal vertical axis (SVA) has no role in predicting LCL following laminoplasty though patients with low T1 slope (≤20°) and high C2-C7 SVA (>22 mm) had correction of kyphotic deformity following laminoplasty. C2-C7 lordosis, Neck Tilt, cervical range of motion, and thoracic kyphosis has no predictive value for LCL. Lower value of T1 slope (T1S-CL) and CL/T1S has more incidence of developing LCL following laminoplasty. The role of C2-C3 disc angle has not yet been evaluated in patients undergoing laminoplasty. Dynamic extension reserve determines the contraction reserve of SPMLC and lower dynamic extension reserve is associated with higher chances of LCL following laminoplasty.
Conclusions: Cervical lordotic alignment is important in maintaining cervical sagittal balance which ultimately is responsible for global spinal sagittal balance and horizontal gaze. Among various radiological parameters, T1 Slope has been reported to be the most important factor affecting cervical alignment following laminoplasty.
Keywords: C2–C3 disc angle; C2–C7 Cobb's angle; C2–C7 lordosis; C2–C7 sagittal vertical axis; T1 slope; cervical laminoplasty; dynamic extension reserve; loss of cervical lordosis.
Copyright: © 2020 Journal of Craniovertebral Junction and Spine.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Scheer JK, Tang JA, Smith JS, Acosta FL, Jr, Protopsaltis TS, Blondel B, et al. Cervical spine alignment, sagittal deformity, and clinical implications: A review. J Neurosurg Spine. 2013;19:141–59. - PubMed
-
- Ames CP, Blondel B, Scheer JK, Schwab FJ, Le Huec JC, Massicotte EM, et al. Cervical radiographical alignment: Comprehensive assessment techniques and potential importance in cervical myelopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2013;38:S149–60. - PubMed
-
- Lin S, Zhou F, Sun Y, Chen Z, Zhang F, Pan S. The severity of operative invasion to the posterior muscular-ligament complex influences cervical sagittal balance after open-door laminoplasty. Eur Spine J. 2015;24:127–35. - PubMed
-
- Tang JA, Scheer JK, Smith JS, Deviren V, Bess S, Hart RA, et al. The impact of standing regional cervical sagittal alignment on outcomes in posterior cervical fusion surgery. Neurosurgery. 2012;71:662–9. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
