Effect of different Agrobacterium rhizogenes strains for in-vitro hairy root induction, total phenolic, flavonoids contents, antibacterial and antioxidant activity of (Cucumis anguria L.)
- PMID: 33100855
- PMCID: PMC7569140
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.08.050
Effect of different Agrobacterium rhizogenes strains for in-vitro hairy root induction, total phenolic, flavonoids contents, antibacterial and antioxidant activity of (Cucumis anguria L.)
Abstract
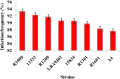
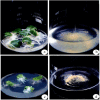
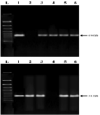
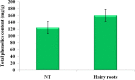
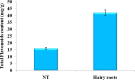
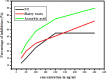
The present study aimed to investigate the effect of different Agrobacterium rhizogenes on the induction of hairy root of Cucumis anguria and determine its total phenolic, flavonoids contents, antibacterial and antioxidant activity. In this investigation A. rhizogenes strains such as, 15834, 13333, A4, R1200, R1000, LBA9402, R1301 and R1601 are all investigated, were developing hairy root conception in cotyledon and leaf tissue explants. Polymerase chain response (PCR) and the converse transcription-PCR are transgenic clones of hairy roots has been utilized rolA and rolB particular primers. In the middle of the different attention of better regulators the extreme transformation frequency was achieved in (IBA + NAA) cotyledon explant. Transgenic hairy roots increase in MS liquid medium added to with IBA + NAA (2.46 + 1.07) displayed the maximum accumulation of biomass 0.68 g/l dry weight (DW) and 6.52 ± 0.49 g/l fresh weight (FW) were obtained at the 21 days of cotyledon explant. The flavonoid and total phenolic contents were estimated using aluminium chloride method and Folin-Ciocalteu method. The amount of phenolic compounds in Cucumis anguria L non transformed root (124.46 ± 6.13 mg GA/g) was lower than that in the methanol extracts of Cucumis anguria L. hairy roots (160.38 ± 5.0 mg GA/g), being was Cucumis anguria L non transformed root lower (42.93 ± 1.58 mg rutin/g) than that in the concentration of total flavonoids in Cucumis anguria L. hairy root (16.26 ± 1.84 mg rutin/g). Additionally, transgenic hairy roots professionally produced various phenolic and flavonoid composites. The total antimicrobial activity, phenolics, flavonoids content and antioxidant were more in the hairy roots related to non-transformed roots. In our discovery, the A. rhizogenes R1000 is promising candidate for hairy root initiation of C. anguria from cotyledone explants were realized large number of hairy roots compared with leaf explants. The antioxidant potential of methanol extracts of flavonoid and phenolic compounds from the hairy roots have great potential to treat various diseases.
Keywords: Agrobacterium rhizogenes; Antibacterial activity; Flavonoid; Hairy roots; Phenolic.
© 2020 The Authors.
Figures
References
-
- Abdullahil Baque M., Hahn E.J., Paek K.Y. Growth, secondary metabolite production and antioxidant enzyme response of Morinda citrifolia adventitious root as affected by auxin and cytokinin. Plant. Biotechnol. Rep. 2010;4:109.
-
- Aoki S., Kawaoka A., Sekine M., Ichikawa T., Fujita T., Shinmyo A., Syono K. The sequence of cellular T-DNA in the genome of Nicotiana glauca that is homologous to ORFs 13 and 14 of the Ri plasmid and the analysis of the expression of the cellular genes in genetic tumors of hybrids between N. glauca and N. langsdorffii. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1994;243(706) - PubMed
-
- Balestri E., Bertini S. Growth and development of Posidoniaoceanica seedlings treated with plant growth regulators: possible implications for meadow restoration. Aquat. Bot. 2003;76:291.
-
- Balvanyos I., Kursinszki L., Szoke E. The effect of plant growth regulators on biomass formation and lobeline production of Lobelia inflata L. hairy root cultures. Plant. Growth Reg. 2001;34:339.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

