Mycobacterium tuberculosis-Specific Antigen Rv3619c Effectively Alleviates Allergic Asthma in Mice
- PMID: 33101014
- PMCID: PMC7546857
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.532199
Mycobacterium tuberculosis-Specific Antigen Rv3619c Effectively Alleviates Allergic Asthma in Mice
Abstract
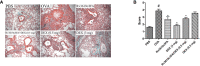
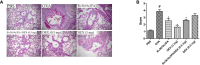
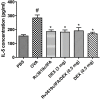
Despite significant advances, asthma remains a cause of premature death, and current treatments are suboptimal. Antigen-specific Th2 cells and their cytokines are primary mediators of the pathophysiological changes seen in asthma. Studies in animal models have shown that mycobacteria can suppress the asthma phenotype by alteration of the Th1/Th2 cytokines ratio. In this study, utilizing a Th1 delivery system to modulate the allergic airway inflammation in a Th2-driven model of asthma, we evaluated the efficacy of immunization with Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific antigen Rv3619c, either alone or in combination with low dose dexamethasone. The rv3619c gene was cloned in an expression plasmid pGES-TH-1, expressed in Escherichia coli, and the recombinant protein Rv3619c was purified to homogeneity using affinity chromatography. Mice were immunized with the recombinant protein emulsified in Freund's Incomplete Adjuvant (IFA) alone and in combination with low dose dexamethasone, and then challenged with ovalbumin (OVA). Airway inflammation was assessed by quantifying airway cytology, histological changes and Th2 cytokine (IL-5) secretion from splenocytes. OVA-specific IgE, IgG and IgG1 from sera was assessed, as well as pERK1/2 expression in the lung tissue. Immunization with recombinant Rv3619c alone inhibited the OVA-induced increase in total cell counts, eosinophil airway cell infiltration in BAL fluid, perivascular and peribronchial inflammation and fibrosis, and goblet cell hyper/metaplasia. In addition, Rv3619c/IFA inhibited the OVA-induced IL-5 in spleen cells, OVA-specific IgE, IgG, and IgG1 levels in sera, and pERK1/2 expression in lung tissue. Immunization with Rv3619c/IFA in combination with low dose dexamethasone resulted in an enhanced effect on some but not all the asthma features. Taken together, this study demonstrates that immunization with Rv3619c/IFA, alone or in combination with dexamethasone, may be an effective treatment strategy for the prevention of asthma.
Keywords: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; Rv3619c; Th1; Th2; asthma; hygiene hypothesis; inflammation; ovalbumin.
Copyright © 2020 Safar, El-Hashim, Amoudy and Mustafa.
Figures

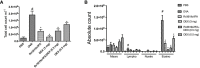


Similar articles
-
The Effect of Delivery Systems on the Induction of T Helper 1 Cell Response to an ESAT6-Like Protein Rv3619c and Identification of Its Immunodominant Peptides.Med Princ Pract. 2022;31(4):359-367. doi: 10.1159/000525136. Epub 2022 May 18. Med Princ Pract. 2022. PMID: 35584661 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of adjuvants and delivery systems on Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cytokine responses in mice immunized with Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific proteins.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 6;15(2):e0228381. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228381. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32027660 Free PMC article.
-
Citrus tachibana Leaves Ethanol Extract Alleviates Airway Inflammation by the Modulation of Th1/Th2 Imbalance via Inhibiting NF-κB Signaling and Histamine Secretion in a Mouse Model of Allergic Asthma.J Med Food. 2017 Jul;20(7):676-684. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2016.3853. Epub 2017 Jun 9. J Med Food. 2017. PMID: 28598706
-
Experimental protocol for development of adjuvant-free murine chronic model of allergic asthma.J Immunol Methods. 2019 May;468:10-19. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2019.03.002. Epub 2019 Mar 14. J Immunol Methods. 2019. PMID: 30880263
-
Bupleurum chinense extract ameliorates an OVA-induced murine allergic asthma through the reduction of the Th2 and Th17 cytokines production by inactivation of NFκB pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Jul;91:1085-1095. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.04.133. Epub 2017 May 16. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28531919
Cited by
-
The Effect of Delivery Systems on the Induction of T Helper 1 Cell Response to an ESAT6-Like Protein Rv3619c and Identification of Its Immunodominant Peptides.Med Princ Pract. 2022;31(4):359-367. doi: 10.1159/000525136. Epub 2022 May 18. Med Princ Pract. 2022. PMID: 35584661 Free PMC article.
-
High protein diet increases the risk of allergic sensitization but not asthma in mice through modulation of the cytokine milieu toward Th2 bias.World Allergy Organ J. 2025 Feb 6;18(2):101031. doi: 10.1016/j.waojou.2025.101031. eCollection 2025 Feb. World Allergy Organ J. 2025. PMID: 39995506 Free PMC article.
-
Immunological Characterization of Proteins Expressed by Genes Located in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-Specific Genomic Regions Encoding the ESAT6-like Proteins.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Jan 7;9(1):27. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9010027. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33430286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemical and Biological Characterization of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis-Specific ESAT6-Like Proteins and their Potentials in the Prevention of Tuberculosis and Asthma.Med Princ Pract. 2023 Sep 13;32(4-5):217-24. doi: 10.1159/000534002. Online ahead of print. Med Princ Pract. 2023. PMID: 37703836 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

