Discovery of Icotinib-1,2,3-Triazole Derivatives as IDO1 Inhibitors
- PMID: 33101032
- PMCID: PMC7555427
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.579024
Discovery of Icotinib-1,2,3-Triazole Derivatives as IDO1 Inhibitors
Abstract
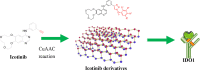
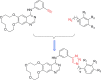
Tumor immunotherapy is considered to be a highlight in cancer treatment in recent years. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) is closely related to the over expression of many cancers, and is therefore a promising target for tumor immunotherapy. To search for novel IDO1-targeting therapeutic agents, 22 icotinib-linked 1,2,3-triazole derivatives were prepared and evaluated for their inhibitory activity against IDO1. The structures of the prepared compounds were confirmed with1H NMR, 13C NMR and HR MS. IDO1 inhibitory activity assay results indicated that 10 of those compounds showed remarkable inhibitory activity against IDO1, among which compound a17 was the most potent with IC50value of 0.37 μM. The binding model between the prepared compounds and IDO1 was studied with molecular modeling study. The current study suggested that icotinib-1,2,3-triazole derivatives could be used as potential inhibitors that preferentially bind to the ferrous form of IDO1 through the formation of coordinate bond with the haem iron.
Keywords: 1,2,3-triazole; icotinib; immunotherapy; indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1; inhibitor.
Copyright © 2020 Mao, Wang, Zhao, Xu, Yao and Li.
Figures


References
-
- Chen S., Guo W., Liu X., Sun P., Wang Y., Ding C., et al. (2019). Design, synthesis and antitumor study of a series of N-Cyclic sulfamoylaminoethyl substituted 1,2,5-oxadiazol-3-amines as new indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 179, 38–55. 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.06.037 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Crosignani S., Bingham P., Bottemanne P., Cannelle H., Cauwenberghs S., Cordonnier M., et al. (2017). Discovery of a novel and selective indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO-1) inhibitor 3-(5-Fluoro-1H-indol-3-yl)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione (EOS200271/PF-06840003) and its characterization as a potential clinical candidate. J. Med. Chem. 60, 9617–9629. 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00974 - DOI - PubMed
-
- De Souza T. B., Caldas I. S., Paula F. R., Rodrigues C. C., Carvalho D. T., Dias D. F. (2020). Synthesis, activity, and molecular modeling studies of 1,2,3-triazole derivatives from natural phenylpropanoids as new trypanocidal agents. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 95, 124–129. 10.1111/cbdd.13628 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

