The Physiology, Pathology, and Therapeutic Interventions for ROCK Isoforms in Diabetic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 33101039
- PMCID: PMC7545791
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.585633
The Physiology, Pathology, and Therapeutic Interventions for ROCK Isoforms in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Abstract
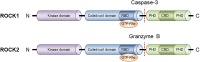
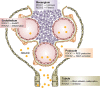
Rho-associated coiled-coil-containing protein kinase (ROCK) is a serine/threonine kinase that was originally identified as RhoA interacting protein. A diverse array of cellular functions, including migration, proliferation, and phenotypic modulation, are orchestrated by ROCK through a mechanism involving cytoskeletal rearrangement. Mammalian cells express two ROCK isoforms: ROCK1 (Rho-kinase β/ROKβ) and ROCK2 (Rho-kinase α/ROKα). While both isoforms have structural similarities and are widely expressed across multiple tissues, investigations in gene knockout animals and cell-based studies have revealed distinct functions of ROCK1 and ROCK2. With respect to the kidney, inhibiting ROCK activity has proven effective for the preventing diabetic kidney disease (DKD) in both type 1 and type 2 diabetic rodent models. However, despite significant progress in the understanding of the renal ROCK biology over the past decade, the pathogenic roles of the ROCK isoforms is only beginning to be elucidated. Recent studies have demonstrated the involvement of renal ROCK1 in mitochondrial dynamics and cellular transdifferentiation, whereas ROCK2 activation leads to inflammation, fibrosis, and cell death in the diabetic kidney. This review provides a conceptual framework for dissecting the molecular underpinnings of ROCK-driven renal injury, focusing on the differences between ROCK1 and ROCK2.
Keywords: ROCK1/ROCK2; Rho (Rho GTPase); diabetic kidney disease (DKD); hypoxia; inflammation; notch.
Copyright © 2020 Matoba, Takeda, Nagai, Sekiguchi, Yokota, Utsunomiya and Nishimura.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ROCK2 regulates TGF-β-induced expression of CTGF and profibrotic genes via NF-κB and cytoskeleton dynamics in mesangial cells.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019 Oct 1;317(4):F839-F851. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00596.2018. Epub 2019 Jul 31. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31364374
-
Rho-associated coiled-coil containing kinases (ROCK): structure, regulation, and functions.Small GTPases. 2014;5:e29846. doi: 10.4161/sgtp.29846. Epub 2014 Jul 10. Small GTPases. 2014. PMID: 25010901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Rho Kinase Isoforms ROCK1 and ROCK2 Each Contribute to the Development of Experimental Pulmonary Fibrosis.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2018 Apr;58(4):471-481. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2017-0075OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29211497 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of both ROCK1 and ROCK2 genes in cardiomyocytes promotes autophagy and reduces cardiac fibrosis during aging.FASEB J. 2019 Jun;33(6):7348-7362. doi: 10.1096/fj.201802510R. Epub 2019 Mar 8. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 30848941 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting ROCK signaling in health, malignant and non-malignant diseases.Immunol Lett. 2020 Mar;219:15-26. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2019.12.012. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Immunol Lett. 2020. PMID: 31904392 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of microRNA-34c reduces detrusor ROCK2 expression and urinary bladder inflammation in experimental cystitis.Life Sci. 2024 Jan 1;336:122317. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.122317. Epub 2023 Nov 29. Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38040245 Free PMC article.
-
Activin A and Cell-Surface GRP78 Are Novel Targetable RhoA Activators for Diabetic Kidney Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 11;22(6):2839. doi: 10.3390/ijms22062839. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33799579 Free PMC article.
-
Effective protective mechanisms of HO-1 in diabetic complications: a narrative review.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Oct 10;10(1):433. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02205-x. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 39389941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of programmed cell death in osteosarcoma: From pathogenesis to therapy.Cancer Med. 2024 May;13(10):e7303. doi: 10.1002/cam4.7303. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 38800967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
G12/13 signaling in asthma.Respir Res. 2024 Aug 2;25(1):295. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-02920-0. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39095798 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boerma M., Fu Q., Wang J., Loose D. S., Bartolozzi A., Ellis J. L., et al. (2008). Comparative gene expression profiling in three primary human cell lines after treatment with a novel inhibitor of Rho kinase or atorvastatin. Blood Coagul. Fibrinol. 19, 709–718. 10.1097/MBC.0b013e32830b2891 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

