Solubility, Stability, and Avidity of Recombinant Antibody Fragments Expressed in Microorganisms
- PMID: 33101218
- PMCID: PMC7546209
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01927
Solubility, Stability, and Avidity of Recombinant Antibody Fragments Expressed in Microorganisms
Abstract
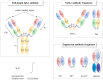
Solubility of recombinant proteins (i.e., the extent of soluble versus insoluble expression in heterogeneous hosts) is the first checkpoint criterion for determining recombinant protein quality. However, even soluble proteins often fail to represent functional activity because of the involvement of non-functional, misfolded, soluble aggregates, which compromise recombinant protein quality. Therefore, screening of solubility and folding competence is crucial for improving the quality of recombinant proteins, especially for therapeutic applications. The issue is often highlighted especially in bacterial recombinant hosts, since bacterial cytoplasm does not provide an optimal environment for the folding of target proteins of mammalian origin. Antibody fragments, such as single-chain variable fragment (scFv), single-chain antibody (scAb), and fragment antigen binding (Fab), have been utilized for numerous applications such as diagnostics, research reagents, or therapeutics. Antibody fragments can be efficiently expressed in microorganisms so that they offer several advantages for diagnostic applications such as low cost and high yield. However, scFv and scAb fragments have generally lower stability to thermal stress than full-length antibodies, necessitating a judicious combination of designer antibodies, and bacterial hosts harnessed with robust chaperone function. In this review, we discuss efforts on not only the production of antibodies or antibody fragments in microorganisms but also scFv stabilization via (i) directed evolution of variants with increased stability using display systems, (ii) stabilization of the interface between variable regions of heavy (V H ) and light (V L ) chains through the introduction of a non-native covalent bond between the two chains, (iii) rational engineering of V H -V L pair, based on the structure, and (iv) computational approaches. We also review recent advances in stability design, increase in avidity by multimerization, and maintaining the functional competence of chimeric proteins prompted by various types of chaperones.
Keywords: antibody fragments; bacterial expression; scFv; solubility; stability.
Copyright © 2020 Kang and Seong.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Production of Stabilized Antibody Fragments in the E. coli Bacterial Cytoplasm and in Transiently Transfected Mammalian Cells.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1904:455-480. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-8958-4_23. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30539486
-
Disrupting the hydrophobic patches at the antibody variable/constant domain interface: improved in vivo folding and physical characterization of an engineered scFv fragment.Protein Eng. 1997 Apr;10(4):435-44. doi: 10.1093/protein/10.4.435. Protein Eng. 1997. PMID: 9194169
-
Humanization of a highly stable single-chain antibody by structure-based antigen-binding site grafting.Mol Immunol. 2008 May;45(9):2474-85. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2008.01.016. Epub 2008 Mar 3. Mol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18313757
-
ScFv Improvement Approaches.Protein Pept Lett. 2018;25(3):222-229. doi: 10.2174/0929866525666171129225436. Protein Pept Lett. 2018. PMID: 29189116 Review.
-
Designer genes: recombinant antibody fragments for biological imaging.Q J Nucl Med. 2000 Sep;44(3):268-83. Q J Nucl Med. 2000. PMID: 11105590 Review.
Cited by
-
Controlled labelling of tracer antibodies for time-resolved fluorescence-based immunoassays.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 5;14(1):18113. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-69294-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39103434 Free PMC article.
-
Fit-for-purpose heterodivalent single-domain antibody for gastrointestinal targeting of toxin B from Clostridium difficile.Protein Sci. 2024 Jul;33(7):e5035. doi: 10.1002/pro.5035. Protein Sci. 2024. PMID: 38923049 Free PMC article.
-
Development of CAR T Cell Therapy in Children-A Comprehensive Overview.J Clin Med. 2022 Apr 12;11(8):2158. doi: 10.3390/jcm11082158. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35456250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lateral flow immunoassay for small-molecules detection in phytoproducts: a review.J Nat Med. 2022 Jun;76(3):521-545. doi: 10.1007/s11418-022-01605-6. Epub 2022 Feb 16. J Nat Med. 2022. PMID: 35171397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A 33-residue peptide tag increases solubility and stability of Escherichia coli produced single-chain antibody fragments.Nat Commun. 2022 Aug 8;13(1):4614. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32423-9. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35941164 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antibody Society (2020). Available online at: https://www.antibodysociety.org/resources/approved-antibodies/ (accessed March 10, 2020).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

