Cytomegalovirus-Mediated T Cell Receptor Repertoire Perturbation Is Present in Early Life
- PMID: 33101265
- PMCID: PMC7554308
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01587
Cytomegalovirus-Mediated T Cell Receptor Repertoire Perturbation Is Present in Early Life
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Cytomegalovirus-Mediated T Cell Receptor Repertoire Perturbation Is Present in Early Life.Front Immunol. 2020 Dec 21;11:633633. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.633633. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33408722 Free PMC article.
Abstract
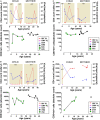
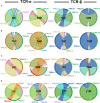
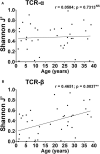
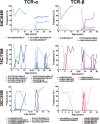
Human cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a highly prevalent herpesvirus, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa, where it is endemic from infancy. The T cell response against CMV is important in keeping the virus in check, with CD8 T cells playing a major role in the control of CMV viraemia. Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) B*44:03-positive individuals raise a robust response against the NEGVKAAW (NW8) epitope, derived from the immediate-early-2 (IE-2) protein. We previously showed that the T cell receptor (TCR) repertoire raised against the NW8-HLA-B*44:03 complex was oligoclonal and characterised by superdominant clones, which were shared amongst unrelated individuals (i.e., "public"). Here, we address the question of how stable the CMV-specific TCR repertoire is over the course of infection, and whether substantial differences are evident in TCR repertoires in children, compared with adults. We present a longitudinal study of four HIV/CMV co-infected mother-child pairs, who in each case express HLA-B*44:03 and make responses to the NW8 epitope, and analyse their TCR repertoire over a period spanning more than 10 years. Using high-throughput sequencing, the paediatric CMV-specific repertoire was found to be highly diverse. In addition, paediatric repertoires were remarkably similar to adults, with public TCR responses being shared amongst children and adults alike. The CMV-specific repertoire in both adults and children displayed strong fluctuations in TCR clonality and repertoire architecture over time. Previously characterised superdominant clonotypes were readily identifiable in the children at high frequency, suggesting that the distortion of the CMV-specific repertoire is incurred as a direct result of CMV infection rather than a product of age-related "memory inflation." Early distortion of the TCR repertoire was particularly apparent in the case of the TCR-β chain, where oligoclonality was low in children and positively correlated with age, a feature we did not observe for TCR-α. This discrepancy between TCR-α and -β chain repertoire may reflect differential contribution to NW8 recognition. Altogether, the results of the present study provide insight into the formation of the TCR repertoire in early life and pave the way to better understanding of CD8 T cell responses to CMV at the molecular level.
Keywords: HLA-B*44:03; T cell receptor; T cell receptor repertoire; cytomegalovirus; memory inflation; paediatric repertoire; repertoire dynamics; superdominance.
Copyright © 2020 Attaf, Roider, Malik, Rius Rafael, Dolton, Predergast, Leslie, Ndung'u, Kløverpris, Sewell and Goulder.
Figures
References
-
- Broers AE, van Der Holt R, van Esser JW, Gratama JW, Henzen-Logmans S, Kuenen-Boumeester V, et al. Increased transplant-related morbidity and mortality in CMV-seropositive patients despite highly effective prevention of CMV disease after allogeneic T-cell-depleted stem cell transplantation. Blood. (2000) 95:2240–5. 10.1182/blood.V95.7.2240.007k08_2240_2245 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

