Association of Clinical Phenotypes in Haploinsufficiency A20 (HA20) With Disrupted Domains of A20
- PMID: 33101300
- PMCID: PMC7546856
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.574992
Association of Clinical Phenotypes in Haploinsufficiency A20 (HA20) With Disrupted Domains of A20
Abstract
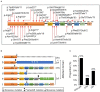
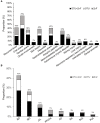
Background: Haploinsufficiency A20 (HA20) is a newly described monogenic disease characterized by a wide spectrum of manifestations and caused by heterozygous mutations in TNFAIP3 which encodes A20 protein. TNFAIP3 mutation leads to disruption of the A20 ovarian tumor (OTU) domain and/or the zinc finger (ZnF) domain. This study aims at exploring the association between the various manifestations of HA20 and different domains disruption of A20. Methods: We reviewed the HA20 cases in previous literature and summarized the clinical features, TNFAIP3 mutation loci and the disrupted domains caused by different sites and patterns of mutations. Patients were classified into three groups according to the A20 domains disruption. Results: A total of 89 patients from 39 families with a genetic diagnosis of HA20 were included. Overall, the age at onset of HA20 was early (median:5.92, IQR:1-10). Patients in the ZnF group showed the earliest onset (median:2.5, IQR:0.6-5), followed by patients in the OTU+ZnF group (median:6, IQR:1-10) and patients in the OTU group (median:10, IQR:8-14). The main manifestations of HA20 patients were recurrent oral ulcers (70%), recurrent fever (42%), gastrointestinal ulcers (40%), skin lesion (38%), genital ulcers (36%), and musculoskeletal disorders (34%). The percentage of patients with musculoskeletal disorders was significantly different among the three groups (p = 0.005). Patients in the OTU+ZnF group and ZnF group were more likely to develop musculoskeletal disorders than patients in the OTU group (p = 0.002 and p = 0.035, respectively). Besides, forty-three percent of HA20 patients were initially diagnosed as Behcet's disease (BD). Compared to the ZnF group, the OTU+ZnF group and OTU group had a higher percentage of patients initially diagnosed as BD (p = 0.006 and p < 0.001, respectively). Conclusion: HA20 is characterized by early-onset and the most common symptoms of HA20 are recurrent oral ulcers, fever and gastrointestinal ulcers. The onset of HA20 in patients with the ZnF domain disruption is earlier than patients with the OTU domain disruption. Compared to the OTU domain, the ZnF domain may be more closely related to musculoskeletal disorders.
Keywords: OTU domain; TNFAIP3; ZnF domain; autoinflammatory disorders; clinical manifestation; haploinsufficiency A20; monogenic disease.
Copyright © 2020 Chen, Ye, Chen, Qin, Seidler, Tian and Xiao.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

