Intracytoplasmic Expression of IL-6 and IL-17A in Circulating CD4+ T Cells Are Strongly Associated with and Predict Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Case-Control Study in Ghana
- PMID: 33101416
- PMCID: PMC7568150
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/2808413
Intracytoplasmic Expression of IL-6 and IL-17A in Circulating CD4+ T Cells Are Strongly Associated with and Predict Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Case-Control Study in Ghana
Abstract
Background: T cell cytokines play important roles in the development and progression of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Loss of Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg balance has been reported in several inflammatory autoimmune diseases. However, their role in RA within hitherto rare Ghanaian context has not been explored. Here, we evaluated the intracytoplasmic CD4+ T cell cytokine patterns in rheumatoid arthritis patients in Ghana and determined their relationship with disease activity.
Methods: This case-control study included 48 newly diagnosed RA patients and 30 apparent healthy controls from two major hospitals in Ghana. Validated structured questionnaires were administered to obtain demographic data; blood samples were collected and processed for flow cytometric analysis.
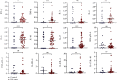
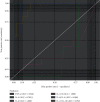
Results: IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, IL-17A, IL-6/IL-4, and IL-17/IL-10 expressions were significantly higher in RA cases compared to the healthy controls. The expression of IL-6 (0.00 (0.00-0.98) vs. 0.82 (0.34-1.10) vs. 1.56 (1.39-1.68), p < 0.0001), IL-17A (0.00 (0.00-0.02) vs. 0.19 (0.09-0.30) vs. 0.99 (0.64-1.25), p < 0.0001), and IL-17A/IL-10 (0.00 (0.00-0.39) vs. 0.15 (0.09-0.26) vs. 0.88 (0.41-1.47), p < 0.0001) increased significantly from the healthy controls through RA patients with low DAS scores to RA patients with moderate DAS scores. IL-6 (β = 0.681, r 2 = 0.527, p < 0.0001), IL-17A (β = 0.770, r 2 = 0.593, p < 0.0001), and IL-17A/IL-10 (β = 0.677, r 2 = 0.452, p < 0.0001) expressions were significantly directly associated with DAS28 scores. IL-6 (cutoff = 1.32, sensitivity = 100.0%, specificity = 100.0%, accuracy = 100.0%, and AUC = 1.000) and IL-17A (cutoff = 0.58, sensitivity = 100.0%, specificity = 100.0%, accuracy = 100.0%, and AUC = 1.000) presented with the best discriminatory power in predicting moderate DAS scores from low DAS scores.
Conclusion: Th1- and Th17-related cytokines predominate in the pathophysiology of RA, with IL-6 and IL-17 being principally and differentially expressed based on the severity of the disease. IL-6 and IL-17A could serve as useful prognostic and disease-monitoring markers in RA in the African context.
Copyright © 2020 Samuel Asamoah Sakyi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Receptors expressions on peripheral lymphocytes and CD4+ CD183+ as a diagnostics biomarker for rheumatoid arthritis: A case-control study in Ghana.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023 Aug;11(8):e976. doi: 10.1002/iid3.976. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023. PMID: 37647423 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Th17 and Th1 cells expressing CD161 are associated with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis.Scand J Rheumatol. 2014;43(3):194-201. doi: 10.3109/03009742.2013.846407. Epub 2014 Jan 7. Scand J Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 24392804
-
IL-22+ CD4+ T cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Int J Rheum Dis. 2013 Oct;16(5):518-26. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.12099. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Int J Rheum Dis. 2013. PMID: 24164838
-
IL-17/Th17 targeting: on the road to prevent chronic destructive arthritis?Cytokine. 2008 Feb;41(2):84-91. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2007.09.014. Epub 2007 Nov 26. Cytokine. 2008. PMID: 18039580 Review.
-
Role of interleukin-23 as a biomarker in rheumatoid arthritis patients and its correlation with disease activity.Int Immunopharmacol. 2016 Feb;31:105-8. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2015.12.011. Epub 2015 Dec 19. Int Immunopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26709220 Review.
Cited by
-
Profiling vitamin D, its mediators and proinflammatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis: A case-control study.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2022 Aug;10(8):e676. doi: 10.1002/iid3.676. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2022. PMID: 35894711 Free PMC article.
-
The role of IL-18 in addition to Th17 cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis development and treatment in women.Sci Rep. 2021 Jul 28;11(1):15391. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-94841-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34321563 Free PMC article.
-
1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 Supplementation during Pregnancy Is Associated with Allergic Rhinitis in the Offspring by Modulating Immunity.J Immunol Res. 2021 Apr 14;2021:6638119. doi: 10.1155/2021/6638119. eCollection 2021. J Immunol Res. 2021. PMID: 33954205 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and verification of a nomogram and a preliminary study on predicting the clinical response of conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs) in rheumatoid arthritis patients.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Dec;10(24):1365. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-5791. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36660697 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

