Antioxidant Effect of Beer Polyphenols and Their Bioavailability in Dental-Derived Stem Cells (D-dSCs) and Human Intestinal Epithelial Lines (Caco-2) Cells
- PMID: 33101420
- PMCID: PMC7569455
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/8835813
Antioxidant Effect of Beer Polyphenols and Their Bioavailability in Dental-Derived Stem Cells (D-dSCs) and Human Intestinal Epithelial Lines (Caco-2) Cells
Abstract
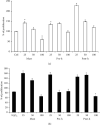
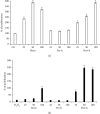
Beer is one of the most consumed alcoholic beverages in the world, rich in chemical compounds of natural origin with high nutritional and biological value. It is made up of water, barley malt, hops, and yeast. The main nutrients are carbohydrates, amino acids, minerals, vitamins, and other compounds such as polyphenols which are responsible for the many health benefits associated with this consumption of drinks. Hops and malt are one of the raw materials for beer and are a source of phenolic compounds. In fact, about 30% of the polyphenols in beer comes from hops and 70%-80% from malt. Natural compounds of foods or plants exert an important antioxidant activity, counteracting the formation of harmful free radicals. In the presence of an intense stressing event, cells activate specific responses to counteract cell death or senescence which is known to act as a key-task in the onset of age-related pathologies and in the loss of tissue homeostasis. Many studies have shown positive effects of natural compounds as beer polyphenols on biological systems. The main aims of our research were to determine the polyphenolic profile of three fractions, coming from stages of beer production, the mashing process (must), the filtration process (prehopping solution), and the boiling process with the addition of hops (posthopping solution), and to evaluate the effects of these fractions on Dental-derived Stem Cells (D-dSCs) and human intestinal epithelial lines (Caco-2 cells). Furthermore, we underline the bioavailability of beer fraction polyphenols by carrying out the in vitro intestinal absorption using the Caco-2 cell model. We found an antioxidant, proliferating, and antisenescent effects of the fractions deriving from the brewing process on D-dSCs and Caco-2 cells. Finally, our results demonstrated that the bioavailability of polyphenols is greater in beer than in the control standards used, supporting the future clinical application of these compounds as potential therapeutic tools in precision and translational medicine.
Copyright © 2020 Marina Di Domenico et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Wine or Beer? Comparison, Changes and Improvement of Polyphenolic Compounds during Technological Phases.Molecules. 2020 Oct 27;25(21):4960. doi: 10.3390/molecules25214960. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33120907 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physiological Mechanisms by Which the Functional Ingredients in Beer Impact Human Health.Molecules. 2024 Jun 29;29(13):3110. doi: 10.3390/molecules29133110. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38999065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of malt source on beer chemistry, flavor, and flavor stability.Food Res Int. 2018 Nov;113:487-504. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.07.024. Epub 2018 Jul 18. Food Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30195545
-
Enzymatic Properties of endo-1,4-β-xylanase from Wheat Malt.Protein Pept Lett. 2019;26(5):332-338. doi: 10.2174/0929866526666190228144851. Protein Pept Lett. 2019. PMID: 30816076
-
Application and possible benefits of high hydrostatic pressure or high-pressure homogenization on beer processing: A review.Food Sci Technol Int. 2017 Oct;23(7):561-581. doi: 10.1177/1082013217714670. Epub 2017 Jun 12. Food Sci Technol Int. 2017. PMID: 28605941 Review.
Cited by
-
Mediterranean Diet and Melatonin: A Systematic Review.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jan 24;12(2):264. doi: 10.3390/antiox12020264. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36829823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Sulfhydryl (Thiols) Groups in Oral and Periodontal Diseases.Biomedicines. 2024 Apr 16;12(4):882. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12040882. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38672236 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery: A Systematic Review of Clinical Applications and Regenerative Outcomes.J Clin Med. 2025 May 22;14(11):3623. doi: 10.3390/jcm14113623. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40507385 Free PMC article. Review.
-
UHPLC-MS/MS Analysis on Flavonoids Composition in Astragalus membranaceus and Their Antioxidant Activity.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Nov 22;10(11):1852. doi: 10.3390/antiox10111852. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34829723 Free PMC article.
-
2,4-di-tert-butylphenol exposure impairs osteogenic differentiation.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 15;461:116386. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2023.116386. Epub 2023 Jan 20. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36682590 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chatterjee N., Kiran S., Ram B. M., Islam N., Ramasarma T., Ramakrishna G. Diperoxovanadate can substitute for H2O2 at much lower concentration in inducing features of premature cellular senescence in mouse fibroblasts (NIH3T3) Mechanisms of Ageing and Development. 2011;132(5):230–239. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2011.04.005. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

