Network Pharmacology Identifies the Mechanisms of Sang-Xing-Zhi-Ke-Fang against Pharyngitis
- PMID: 33101439
- PMCID: PMC7576344
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/2421916
Network Pharmacology Identifies the Mechanisms of Sang-Xing-Zhi-Ke-Fang against Pharyngitis
Abstract
Background: Sang-Xing-Zhi-Ke-Fang (SXZKF) demonstrates good therapeutic effect against pharyngitis. Nevertheless, the pharmacological mechanism underlying its effectiveness is still unclear.
Objective: To investigate the underlying mechanisms of SXZKF against pharyngitis using network pharmacology method.
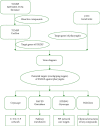
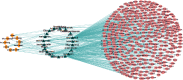
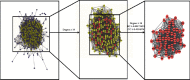
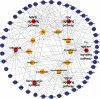
Methods: Bioactive ingredients of SXZKF were collected and screened using published literature and two public databases. Using four public databases, the overlapping genes between these bioactive compound-related and pharyngitis-related genes were identified by Venn diagram. Protein-protein interaction (PPI) was obtained using "Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes (STRING)" database. "Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery ver. 6.8 (DAVID 6.8)" was used to perform Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis to explore the molecular mechanisms of SXZKF against pharyngitis. Finally, Cytoscape 3.7.2 software was used to construct and visualize the networks.
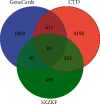
Result: A total of 102 bioactive compounds were identified. Among them, 886 compounds-related and 6258 pharyngitis-related genes were identified, including 387 overlapping genes. Sixty-three core targets were obtained, including ALB, PPARγ, MAPK3, EGF, and PTGS2. Signaling pathways closely related to mechanisms of SXZKF for pharyngitis were identified, including serotonergic synapse, VEGF signaling pathway, Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway, Ras signaling pathway, MAPK signaling pathway, and influenza A.
Conclusion: This is the first identification of in-depth study of SXZKF against pharyngitis using network pharmacology. This new evidence could be informative in providing new support on the clinical effects of SXZKF on pharyngitis and for the development of personalized medicine for pharyngitis.
Copyright © 2020 Yinhe Deng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exploring the mechanism of Shenqisherong pill against cervical spondylotic myelopathy by network pharmacology and molecular docking.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Oct;10(10):10253-10275. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-408. Epub 2021 Aug 26. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 34498478
-
Network pharmacology-based strategy to investigate pharmacological mechanisms of Tinospora sinensis for treatment of Alzheimer's disease.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Sep 15;259:112940. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112940. Epub 2020 May 7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32389853
-
Isolation and identification of the components in Cybister chinensis Motschulsky against inflammation and their mechanisms of action based on network pharmacology and molecular docking.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Mar 1;285:114851. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114851. Epub 2021 Nov 19. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34808299
-
Network Pharmacology-Based Prediction of Active Ingredients and Mechanisms of Lamiophlomis rotata (Benth.) Kudo Against Rheumatoid Arthritis.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Nov 27;10:1435. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01435. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31849678 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of the mechanism of Zisheng Shenqi decoction against gout arthritis using network pharmacology.Comput Biol Chem. 2021 Feb;90:107358. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107358. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Comput Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33243703 Review.
Cited by
-
The Imbalance of Mitochondrial Homeostasis of Peripheral Blood-Derived Macrophages Mediated by MAFLD May Impair the Walking Ability of Elderly Patients with Osteopenia.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Mar 24;2022:5210870. doi: 10.1155/2022/5210870. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35368864 Free PMC article.
-
Network Pharmacology-Based Investigation on the Mechanism of the JinGuanLan Formula in Treating Acne Vulgaris.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jul 13;2022:6944792. doi: 10.1155/2022/6944792. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35873639 Free PMC article.
-
Gegen Qinlian Decoction Ameliorates Hyperuricemia-Induced Renal Tubular Injury via Blocking the Inflammatory Signaling Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2021 May 4;12:665398. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.665398. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34017258 Free PMC article.
-
Gegen Qinlian Decoction treatment of asymptomatic hyperuricemia by targeting circadian immune function.Chin Med. 2023 Jun 27;18(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s13020-023-00775-z. Chin Med. 2023. PMID: 37370132 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yao X. Y., Bian Y. J., Gao Y., et al. Clinical application evaluation and revision suggestions of clinical practice guideline on traditional Chinese medicine therapy alone or combined with antibiotics for acute pharyngitis. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi = Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi = China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica. 2018;43(24):4765–4770. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20181009.009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Li C. X., Wu F. C., Yuan W. L., et al. Systematic review of herbal tea (a traditional Chinese treatment method) in the therapy of chronic simple pharyngitis and preliminary exploration about its medication rules. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2019;2019 doi: 10.1155/2019/9458676.9458676 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

