Esomeprazole affects the proliferation, metastasis, apoptosis and chemosensitivity of gastric cancer cells by regulating lncRNA/circRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA networks
- PMID: 33101498
- PMCID: PMC7577076
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2020.12193
Esomeprazole affects the proliferation, metastasis, apoptosis and chemosensitivity of gastric cancer cells by regulating lncRNA/circRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA networks
Abstract
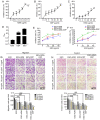
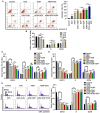
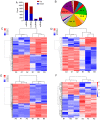
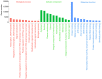
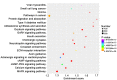
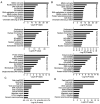
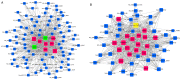
Recently, proton pump inhibitors have become a hot research topic in the field of cancer drug research. However, the specific anti-tumor effect and underlying mechanisms of esomeprazole (ESO) in gastric cancer (GC) have remained elusive. In the present study, the toxic effects of ESO on the GC cell line AGS were investigated. MTT assays confirmed that ESO inhibited the proliferation of AGS cells and significantly enhanced their chemosensitivity. Transwell assays were performed to determine the anti-metastatic effects of ESO in AGS cells. Flow cytometry demonstrated that ESO induced cell apoptosis and caused cell cycle arrest in the S and G2/M phases. Furthermore, the differential expression of 948 long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), 114 circular RNAs (circRNAs), 1,197 mRNAs and 199 microRNAs (miRNAs) was detected in AGS cells via microarray analysis and RNA-sequencing. The top 10 differently expressed genes were mostly located on chromosomes 10 and 19. In addition, Gene Ontology analysis indicated that the genes were accumulated in functional terms associated with DNA replication, the cell cycle and the apoptotic signaling pathway. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway analysis revealed a variety of significantly dysregulated signaling pathways and targets, including the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance pathway, forkhead box O signaling pathway, p53 signaling pathway and platinum drug resistance pathway. Subsequently, the interactions of microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2), homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 2 (HIPK2) and ankyrin 2 (ANK2) were noted in a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) network, which may be important targets of ESO, exerting an anti-tumor effect in AGS cells. Collectively, ESO affects the proliferation, metastasis, apoptosis and chemosensitivity of gastric cancer cells by regulating long non-coding RNA/circRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA networks.
Keywords: apoptosis; chemosensitivity; competing endogenous RNA; esomeprazole; gastric cancer; metastasis; proliferation.
Copyright: © Xu et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transcriptomic analysis of high-throughput sequencing about circRNA, lncRNA and mRNA in bladder cancer.Gene. 2018 Nov 30;677:189-197. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.07.041. Epub 2018 Jul 17. Gene. 2018. PMID: 30025927
-
Comprehensive analysis of the whole coding and non-coding RNA transcriptome expression profiles and construction of the circRNA-lncRNA co-regulated ceRNA network in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.Funct Integr Genomics. 2019 Jan;19(1):109-121. doi: 10.1007/s10142-018-0631-y. Epub 2018 Aug 21. Funct Integr Genomics. 2019. PMID: 30128795
-
Identification of circular RNA-associated competing endogenous RNA network in the development of cleft palate.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Sep;120(9):16062-16074. doi: 10.1002/jcb.28888. Epub 2019 May 9. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31074068
-
Epigenetic Associations between lncRNA/circRNA and miRNA in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Sep 14;12(9):2622. doi: 10.3390/cancers12092622. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32937886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reconstruction and Analysis of the Differentially Expressed IncRNA-miRNA-mRNA Network Based on Competitive Endogenous RNA in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2019;29(6):539-549. doi: 10.1615/CritRevEukaryotGeneExpr.2019028740. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2019. PMID: 32422009 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of exosomal competing endogenous RNA network response to paclitaxel treatment reveals key genes in advanced gastric cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 25;12:1027748. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1027748. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36387235 Free PMC article.
-
The Regulatory Network of Gastric Cancer Pathogenesis and Its Potential Therapeutic Active Ingredients of Traditional Chinese Medicine Based on Bioinformatics, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Nov 26;2022:5005498. doi: 10.1155/2022/5005498. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 36471693 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Network Analysis of microRNAs, mRNAs, and Proteins Reveals the Regulatory Interaction between hsa-mir-200b and CFL2 Associated with Advanced Stage and Poor Prognosis in Patients with Intestinal Gastric Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 12;15(22):5374. doi: 10.3390/cancers15225374. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38001634 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Coding RNA as Biomarkers and Their Role in the Pathogenesis of Gastric Cancer-A Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 9;25(10):5144. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105144. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LINC01088 regulates the miR-95/LATS2 pathway through the ceRNA mechanism to inhibit the growth, invasion and migration of gastric cancer cells.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2022 Jan-Dec;36:3946320221108271. doi: 10.1177/03946320221108271. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35728587 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Song YH, He L, Wang YL, Wu Q, Huang WZ. Molecularly targeted therapy and immunotherapy for hormone Receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer (Review) Oncol Rep. 2020;44:3–13. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
