Association of VPREB1 Gene Copy Number Variation and Rheumatoid Arthritis Susceptibility
- PMID: 33101545
- PMCID: PMC7568136
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/7189626
Association of VPREB1 Gene Copy Number Variation and Rheumatoid Arthritis Susceptibility
Abstract
Objective: Copy number variation (CNV) is a structural variation in the human genome that has been associated with multiple clinical phenotypes. B cells are important components of rheumatoid arthritis- (RA-) mediated immune response; hence, CNV in the regulators of B cells (such as VPREB1) can influence RA susceptibility. In this study, we aimed to explore the association of CNV in the VPREB1 gene with RA susceptibility in the Pakistani population.
Methods: A total of 1,106 subjects (616 RA cases, 490 healthy controls) were selected from three rheumatology centers in Pakistan. VPREB1 CNV was determined using the TaqMan® CN assay (Hs02879734_cn, Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA), and CNV was estimated by using CopyCaller® (version 2.1; Applied Biosystems, USA) software. Odds ratio (OR) was calculated by logistic regression with sex and age as covariates in R.
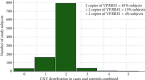
Results: A significant association between >2 VPREB1 CNV and RA risk was observed with an OR of 3.92 (95% CI: 1.27 - 12.12; p = 0.01746) in the total sample. Whereas <2 CNV showed a significantly protective effect against RA risk in women with an OR of 0.48 (95% CI: 0.29-0.79; p = 0.00381).
Conclusion: CNV > 2 of VPREB1 is a risk factor for RA in the total Pakistani population, while CNV < 2 is protective in women.
Copyright © 2020 Muhammad Muaaz Aslam et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Feuk L., Carson A. R., Scherer S. W. Structural variation in the human genome. Nature Reviews Genetics. 2006;7:p. 85. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases