Pleural metastasis of anaplastic meningioma
- PMID: 33101563
- PMCID: PMC7577895
- DOI: 10.1016/j.radcr.2020.10.020
Pleural metastasis of anaplastic meningioma
Abstract
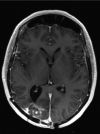
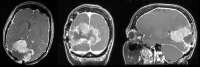
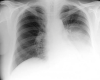
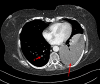
A 52-year-old woman presented to the emergency department with several days of progressive dyspnoea and thoracic pain. Her medical history included a (recurrent) anaplastic meningioma, for which she was treated with surgery and radiotherapy. A chest X-ray showed occurrence of total opacification of the left lower lobe and a chest computed tomography demonstrated a pleural mass of 12 × 9 × 15 cm in the left lower lobe. Biopsy of the pleural mass revealed a metastasis of the patient's anaplastic meningioma. Extracranial metastases from meningioma are extremely uncommon (≤ 0.1%-0.2% of cases), but important for a patient's prognosis.
Keywords: Anaplastic meningioma; Pleural metastasis.
© 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. on behalf of University of Washington.
Figures

References
-
- Riemenschneider MJ, Perry A, Reifenberger G. Histological classification and molecular genetics of meningiomas. Lancet Neurol. 2006;5:1045–1054. - PubMed
-
- Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, von Deimling A, Figarella-Branger D, Cavenee WK. The 2016 World Health Organization classification of tumors of the central nervous system: a summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016;131:803–820. - PubMed
-
- Apra C, Peyre M, Kalamarides M. Expert Rev Neurother. 2018;18(3):241-249. - PubMed
-
- Goldbrunner R, Minniti G, Preusser M, Jenkinson MD, Sallabanda K, Houdart E. EANO guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of meningiomas. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17:e383–e391. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

