Accuracy of WASCA Aberrometer Refraction Compared to Manifest Refraction and Cycloplegic Refraction in Hyperopia Measurement
- PMID: 33101782
- PMCID: PMC7545064
- DOI: 10.1167/tvst.9.11.5
Accuracy of WASCA Aberrometer Refraction Compared to Manifest Refraction and Cycloplegic Refraction in Hyperopia Measurement
Abstract
Purpose: To explore the agreement between the wavefront supported custom ablation (WASCA) aberrometer and manifest refraction (MR) and cycloplegic refraction (CR) in hyperopia testing.
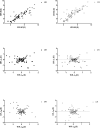
Methods: Ninety eyes of 90 hyperopic patients (spherical equivalent ≥ +0.5 D) were evaluated; MR, CR, and WASCA refraction (WR) were performed consecutively. Analysis pupil size was 6.0 mm in WASCA measurement using the Seidel method. The conventional notation was transferred into vector components for analysis, i.e., spherical equivalent (M) and two cross-cylinders at axis 0° (J0) and axis 45° (J45). Bland-Altman plots were used to test the agreement between the two measurements.
Results: The mean Ms obtained with MR and CR were 3.23 ± 1.74 D and 4.04 ± 2.04 D, respectively (P < 0.001), and the correlation was high (r = 0.90, P < 0.001). The WR was highly correlated with MR and CR in terms of M (r = 0.89, 0.87), but not significantly correlated in J0 and J45. The total dioptric power vector error was 0.18 ± 1.00 D between WR and MR and -0.64 ± 1.03 D between WR and CR. The limits of agreement of all vector components were beyond ± 1.0 D. With hyperopia level increase, WR tended to overestimate MR (P = 0.04), whereas WR always underestimated CR.
Conclusions: WASCA could act as a reference of subjective refraction in hyperopia measurement, the exchangeability is not fully applicable.
Translational relevance: WASCA can provide an alternative for objective refraction in hyperopia measurement.
Keywords: WASCA; agreement; hyperopia; subjective refraction.
Copyright 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: D. Fu, None; X. Ding, None; J. Shang, None; Z. Yu, None; X. Zhou, None
Figures

References
-
- Neroev VV, Tarutta EP, Arutyunyan SG, Khandzhyan AT, Khodzhabekyan NV. [Wavefront aberrations and accommodation in myopes and hyperopes]. Vestn Oftalmol. 2017; 133: 5–9. - PubMed
-
- Liang J, Grimm B, Goelz S, Bille JF. Objective measurement of wave aberrations of the human eye with the use of a Hartmann-Shack wave-front sensor. J Opt Soc Am A Opt Image Sci Vis. 1994; 11: 1949–1957. - PubMed
-
- Reinstein DZ, Morral M, Gobbe M, Archer TJ. Accuracy of refractive outcomes in myopic and hyperopic laser in situ keratomileusis: manifest versus aberrometric refraction. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38: 1989–1995. - PubMed
-
- Zhu X, Dai J, Chu R, Lu Y, Zhou X, Wang L. Accuracy of WASCA aberrometer refraction compared to manifest refraction in Chinese adult myopes. J Refract Surg. 2009; 25: 1026–1033. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

