Adductor Canal Block Duration of Analgesia Successfully Prolonged With Perineural Dexmedetomidine and Dexamethasone in Addition to IPACK Block for Total Knee Arthroplasty
- PMID: 33101812
- PMCID: PMC7577298
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.10566
Adductor Canal Block Duration of Analgesia Successfully Prolonged With Perineural Dexmedetomidine and Dexamethasone in Addition to IPACK Block for Total Knee Arthroplasty
Erratum in
-
Correction: Adductor Canal Block Duration of Analgesia Successfully Prolonged With Perineural Dexmedetomidine and Dexamethasone in Addition to IPACK Block for Total Knee Arthroplasty.Cureus. 2020 Nov 16;12(11):c39. doi: 10.7759/cureus.c39. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 33209562 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is among the most commonly performed orthopedic procedures. Controlling the pain of this patient population is essential in improving outcomes such as opioid consumption, hospital length of stay, overall function, and rehabilitation participation following their procedure. Local anesthetic infiltration of the interspace between the popliteal artery and capsule of the posterior knee, known as the IPACK block, combined with an adductor canal block (ACB) can be used to reduce pain in the challenging area of the posterior knee after knee surgery without compromising motor function of the quadriceps muscles. One limiting factor to this combination of techniques is the duration of analgesia provided. This case series demonstrates the combination of dexmedetomidine and dexamethasone (Dex-Dex) as local anesthetic adjuvants to significantly prolong the analgesic duration of ACB (in addition to IPACK block) in three patients undergoing TKA. Preoperative ACB and IPACK blocks were performed for postoperative analgesia in three TKA patients. The anesthetic mixture was 10 cc 0.2% ropivacaine combined with 25 mcg of dexmedetomidine and 5-mg preservative-free dexamethasone for the ACB, and 0.2% ropivacaine combined with 5-mg preservative-free dexamethasone was utilized for the IPACK block. Two of the patients reported experiencing four days of analgesia and one patient reported five days of analgesia following the ACB + IPACK block. Two of the patients required no opioid analgesics postoperatively. An ACB utilizing 0.75% ropivacaine has been demonstrated to provide approximately 10.8 hours of analgesia. Our series demonstrates a significantly prolonged duration of analgesia from this injectate combination. Few studies have utilized the Dex-Dex combination. The combination, however, was previously proven to safely increase the analgesic duration of a caudal block prior to hypospadias surgeries in pediatrics. More studies are needed to understand a potential synergistic effect of Dex-Dex, which could have a substantial impact on postoperative analgesia for TKA patients.
Keywords: adductor canal block; dexamethasone; dexmedetomidine; ipack block; pain management; regional anesthesia; total knee arthroplasty.
Copyright © 2020, Herman et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
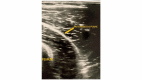
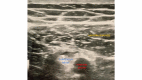
Similar articles
-
iPACK block (local anesthetic infiltration of the interspace between the popliteal artery and the posterior knee capsule) added to the adductor canal blocks versus the adductor canal blocks in the pain management after total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2022 Aug 12;17(1):387. doi: 10.1186/s13018-022-03272-5. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022. PMID: 35962410 Free PMC article.
-
Adductor Canal Block Combined With iPACK (Interspace Between the Popliteal Artery and the Capsule of the Posterior Knee) Block vs Periarticular Injection for Analgesia After Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Randomized Noninferiority Trial.J Arthroplasty. 2021 Jan;36(1):122-129.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2020.06.086. Epub 2020 Jul 2. J Arthroplasty. 2021. PMID: 32694032 Clinical Trial.
-
Continuous adductor canal block is superior to adductor canal block alone or adductor canal block combined with IPACK block (interspace between the popliteal artery and the posterior capsule of knee) in postoperative analgesia and ambulation following total knee arthroplasty: randomized control trial.Musculoskelet Surg. 2022 Jun;106(2):155-162. doi: 10.1007/s12306-020-00682-8. Epub 2020 Sep 27. Musculoskelet Surg. 2022. PMID: 32980982 Clinical Trial.
-
Adding Dexamethasone to Adductor Canal Block Combined With iPACK Block Improve Postoperative Analgesia of Total Knee Arthroplasty.Clin J Pain. 2022 Sep 1;38(9):575-581. doi: 10.1097/AJP.0000000000001056. Clin J Pain. 2022. PMID: 35819163 Clinical Trial.
-
Does the Addition of iPACK Block to Adductor Canal Block Provide Improved Analgesic Effect in Total Knee Arthroplasty? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Knee Surg. 2023 Mar;36(4):345-353. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1733882. Epub 2021 Oct 2. J Knee Surg. 2023. PMID: 34600437
Cited by
-
A comparative randomized controlled study of modified 4 in 1 block versus IPACK plus adductor canal block for post-operative analgesia in total knee arthroplasty.Indian J Anaesth. 2023 Mar;67(3):296-301. doi: 10.4103/ija.ija_530_22. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Indian J Anaesth. 2023. PMID: 37250512 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Single-Shot Infiltration Between the Popliteal Artery and Capsule of the Knee and Adductor Canal Block With Bupivacaine, Dexmedetomidine, and Dexamethasone for Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Propensity-Matched Analysis.Arthroplast Today. 2023 Dec 28;25:101292. doi: 10.1016/j.artd.2023.101292. eCollection 2024 Feb. Arthroplast Today. 2023. PMID: 38235397 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of perioperative analgesia between posterior stabilized and posterior cruciate retaining prostheses following total knee arthroplasty.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 12;15(1):25234. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-09364-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40652026 Free PMC article.
-
Local Periarticular Infiltration with Dexmedetomidine Results in Superior Patient Well-Being after Total Knee Arthroplasty Compared with Peripheral Nerve Blocks: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial with a Follow-Up of Two Years.J Clin Med. 2023 Aug 2;12(15):5088. doi: 10.3390/jcm12155088. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37568489 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of pectineus muscle plane block versus femoral nerve block for postoperative analgesia and early recovery after knee surgery: a randomised controlled trial study protocol.BMJ Open. 2024 Jul 27;14(7):e080968. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-080968. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 39067877 Free PMC article.
References
-
- The adductor canal catheter and interspace between the popliteal artery and the posterior capsule of the knee for total knee arthroplasty. Elliott CE, Thobhani S. Tech Reg Anesth Pain Manag. 2014;18:126–129.
-
- Ambulatory knee replacements with IPACK block. Jinadu S, Pai P, Lai Y. J Clin Anesth. 2020;60:55–56. - PubMed
-
- Comparison of adductor canal block and IPACK block (interspace between the popliteal artery and the capsule of the posterior knee) with adductor canal block alone after total knee arthroplasty: a prospective control trial on pain and knee function in immediate postoperative period. Sankineani SR, Reddy ARC, Eachempati KK, Jangale A, Gurava Reddy A V. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2018;28:1391–1395. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
