Multigenerational case examples of hypophosphatasia: Challenges in genetic counseling and disease management
- PMID: 33101980
- PMCID: PMC7578550
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2020.100661
Multigenerational case examples of hypophosphatasia: Challenges in genetic counseling and disease management
Abstract
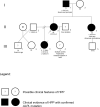
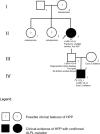
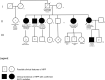
Hypophosphatasia (HPP) is an inherited metabolic condition caused by pathogenic mutations in the ALPL gene. This leads to deficiency of tissue non-specific alkaline phosphatase (TNSALP), resulting in decreased mineralization of the bones and/or teeth and multi-systemic complications. Inheritance may be autosomal dominant or recessive, and the phenotypic spectrum, including age of onset, varies widely. We present four families demonstrating both modes of inheritance of HPP and phenotypic variability and discuss the resultant challenges in disease management, genetic counseling, and risk assessment. Failure to consider different modes of inheritance in a family with HPP may lead to an inaccurate risk assessment upon which medical and reproductive decisions may be made. We highlight the essential role of high-quality genetic counseling and meaningful biochemical and molecular testing strategies in the evaluation and management of families with HPP.
Keywords: ALPL gene; Alkaline phosphatase; Dominant inheritance; Family history; Genetic counseling; Hypophosphatasia; Recessive inheritance.
© 2020 The Authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecular and clinical analysis of ALPL in a cohort of patients with suspicion of Hypophosphatasia.Am J Med Genet A. 2017 Mar;173(3):601-610. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.37991. Epub 2017 Jan 27. Am J Med Genet A. 2017. PMID: 28127875
-
Hypophosphatasia: An overview For 2017.Bone. 2017 Sep;102:15-25. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2017.02.011. Epub 2017 Feb 24. Bone. 2017. PMID: 28238808 Review.
-
Molecular and cellular basis of hypophosphatasia.J Oral Biosci. 2019 Sep;61(3):141-148. doi: 10.1016/j.job.2019.07.003. Epub 2019 Aug 8. J Oral Biosci. 2019. PMID: 31400546 Review.
-
Hypophosphatasia: Biochemical hallmarks validate the expanded pediatric clinical nosology.Bone. 2018 May;110:96-106. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2018.01.022. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Bone. 2018. PMID: 29360619
-
Genetics of hypophosphatasia.Arch Pediatr. 2017 May;24(5S2):5S51-5S56. doi: 10.1016/S0929-693X(18)30014-9. Arch Pediatr. 2017. PMID: 29405932
Cited by
-
A Delphi panel to build consensus on assessing disease severity and disease progression in adult patients with hypophosphatasia in the United States.J Endocrinol Invest. 2024 Jun;47(6):1487-1497. doi: 10.1007/s40618-023-02256-4. Epub 2024 Jan 18. J Endocrinol Invest. 2024. PMID: 38236379 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical profiles of treated and untreated adults with hypophosphatasia in the Global HPP Registry.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2022 Jul 19;17(1):277. doi: 10.1186/s13023-022-02393-8. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2022. PMID: 35854311 Free PMC article.
-
Transition of young adults with metabolic bone diseases to adult care.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 17;14:1137976. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1137976. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37008909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene Therapy Using Adeno-Associated Virus Serotype 8 Encoding TNAP-D10 Improves the Skeletal and Dentoalveolar Phenotypes in Alpl-/- Mice.J Bone Miner Res. 2021 Sep;36(9):1835-1849. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.4382. Epub 2021 Jun 15. J Bone Miner Res. 2021. PMID: 34076297 Free PMC article.
-
TNAP as a New Player in Chronic Inflammatory Conditions and Metabolism.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 18;22(2):919. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020919. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33477631 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Whyte M.P., Leung E., Wilcox W.R., Liese J., Argente J., Martos-Moreno G.Á, Reeves A., Fujita K.P., Moseley S., Hofmann C. Study 011-10 Investigators. Natural History of Perinatal and Infantile Hypophosphatasia: A Retrospective Study. J. Pediatr. 2019;209:116–124.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2019.01.049. (Epub 2019 Apr 9. PMID: 30979546) - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

