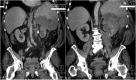
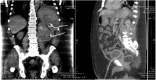
Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis caused by fusobacterium nucleatum. Case report and review of literature
- PMID: 33101996
- PMCID: PMC7573844
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eucr.2020.101293
Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis caused by fusobacterium nucleatum. Case report and review of literature
Abstract
Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritisis (XGP) is a rare and aggressive form of chronic urinary tract infection. The most common microorganism is Proteus but other microorganisms have been described in the literature. In this article, we describe a sixty-year-old male who presented with urosepsis and sever thrombocytopenia secondary to Fusobacterium nucleatum urinary tract infection which led to poorly functioning XGP. The rarity of the microorganism and the devastating clinical course encourages us to report it as anaerobes don't usually cause UTI but unusual microorganism should be suspected if the clinical course is atypical or if urinary tract abnormalities are present.
Keywords: Fusobacterium nucleatum; Renal calculi; Urinary tract infection; XGP.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Tolia B.M., Iloreta A., Freed S.Z., Fruchtman B., Bennett B., Newman H.R. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis: detailed analysis of 29 cases and a brief discussion of atypical presentations. J Urol. 1981 Oct;126(4):437–442. - PubMed
-
- Segura J.W., Kelalis P.P., Martin W.J., Smith L.H. Anaerobic bacteria in the urinary tract. Mayo Clin Proc. 1972 Jan;47(1):30–33. - PubMed
-
- Su C.P., Huang P.Y., Yang C.C., Lee M.H. Fusobacterium bacteremia: clinical significance and outcomes. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2009 Aug;42(4):336–342. - PubMed
-
- Aliyu S.H., Yong P.F., Newport M.J. Molecular diagnosis of Fusobacterium necrophorum infection (Lemierre's syndrome) Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2005 Mar;24(3):226–229. - PubMed
-
- Ribot S., Gal K., Goldblat M.V., Eslami H.H. The role of anaerobic bacteria in the pathogenesis of urinary tract infections. J Urol. 1981 Dec;126(6):852–853. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources