COVID-19 rapid diagnostic test could contain transmission in low- and middle-income countries
- PMID: 33102170
- PMCID: PMC7567180
- DOI: 10.4102/ajlm.v9i1.1255
COVID-19 rapid diagnostic test could contain transmission in low- and middle-income countries
Abstract
Background: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) has impacted heavily on global health. Although real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is the current diagnostic method, challenges for low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) necessitate cheaper, higher-throughput, reliable rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs).
Objective: We reviewed the documented performance characteristics of available COVID-19 RDTs to understand their public health utility in the ongoing pandemic, especially in resource-scarce LMIC settings.
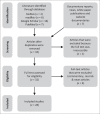
Methods: Using a scoping review methodology framework, common literature databases and documentary reports were searched up to 22 April 2020, irrespective of geographical location. The search terms included 'SARS-CoV-2 AND serological testing' and 'COVID-19 AND serological testing'.
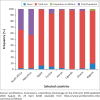
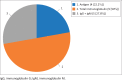
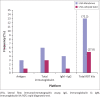
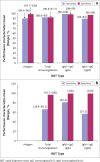
Results: A total of 18 RDTs produced in eight countries, namely China (6; 33.33%), the United States (4; 22.22%), Germany (2; 11.11%), Singapore (2; 11.11%), Canada, Kenya, Korea and Belgium (1 each; 5.56%), were evaluated. Reported sensitivity ranged from 18.4% to 100% (average = 84.7%), whereas specificity ranged from 90.6% to 100% (average = 95.6%). The testing time ranged from 2 min to 30 min. Of the 12 validated RDTs, the IgM/IgG duo kit with non-colloidal gold labelling system was reported to elicit the highest sensitivity (98% - 100%) and specificity (98% - 99% for IgG and 96% - 99% for IgM).
Conclusion: We found reports of high sensitivity and specificity among the developed RDTs that could complement RT-PCR for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies, especially for screening in LMICs. However, it is necessary to validate these kits locally.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus disease; SARS-CoV-2; low- and middle-income countries; rapid diagnostic test.
© 2020. The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cost-effectiveness of COVID rapid diagnostic tests for patients with severe/critical illness in low- and middle-income countries: A modeling study.PLoS Med. 2024 Jul 18;21(7):e1004429. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1004429. eCollection 2024 Jul. PLoS Med. 2024. PMID: 39024370 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of performance of two SARS-CoV-2 Rapid IgM-IgG combined antibody tests on capillary whole blood samples from the fingertip.PLoS One. 2020 Sep 17;15(9):e0237694. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237694. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32941461 Free PMC article.
-
Universal screening for SARS-CoV-2 infection: a rapid review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Sep 15;9(9):CD013718. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013718. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33502003 Free PMC article.
-
A Multicenter Clinical Diagnostic Accuracy Study of SureStatus, an Affordable, WHO Emergency Use-Listed, Rapid, Point-Of-Care Antigen-Detecting Diagnostic Test for SARS-CoV-2.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Oct 26;10(5):e0122922. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01229-22. Epub 2022 Sep 6. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36066256 Free PMC article.
-
The challenges of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) testing in low-middle income countries and possible cost-effective measures in resource-limited settings.Global Health. 2022 Jan 22;18(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s12992-022-00796-7. Global Health. 2022. PMID: 35065670 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Acceptability, Feasibility, and Uptake of COVID-19 Antigen Rapid Diagnostic Self-Testing at the Community Level in Tanzania.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2024 Nov 26;112(4_Suppl):26-36. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.23-0732. Print 2025 Apr 1. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2024. PMID: 39591640 Free PMC article.
-
Considerations for resuming global surgery outreach programs during and after the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic.Surgery. 2021 Nov;170(5):1405-1410. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2021.05.029. Epub 2021 May 25. Surgery. 2021. PMID: 34130811 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluating the Demand for Nucleic Acid Testing in Different Scenarios of COVID-19 Transmission: A Simulation Study.Infect Dis Ther. 2024 Apr;13(4):813-826. doi: 10.1007/s40121-024-00954-x. Epub 2024 Mar 18. Infect Dis Ther. 2024. PMID: 38498107 Free PMC article.
-
Pilot deployment of a community health care worker in distributing and offering the COVID-19 AgRDT in Tanzania.Sci Rep. 2024 May 22;14(1):11679. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-62379-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38778088 Free PMC article.
-
Repeated detection of SARS-CoV-2 in pet dogs in Ibadan, Oyo State, Nigeria: a cause for vigilance.BMC Vet Res. 2025 Mar 22;21(1):196. doi: 10.1186/s12917-025-04647-6. BMC Vet Res. 2025. PMID: 40121457 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
