Metformin and/or vildagliptin mitigate type II diabetes mellitus induced-oxidative stress: The intriguing effect
- PMID: 33102198
- PMCID: PMC7574736
- DOI: 10.4103/japtr.JAPTR_18_20
Metformin and/or vildagliptin mitigate type II diabetes mellitus induced-oxidative stress: The intriguing effect
Abstract
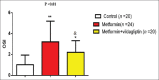
The aim of the present study was to investigate the probable effects of metformin plus vildagliptin on the oxidative stress index (OSI) in patients with type II diabetes mellitus (T2DM). In this case-control study, 44 patients with T2DM on either metformin monotherapy (n = 24) or metformin plus vildagliptin (n = 20) were compared with healthy controls (n = 20). Anthropometric and biochemical variables including body mass index, blood pressure profile, cardiac indices, lipid profile, fasting blood glucose, fasting serum insulin, and glycemic indices were assessed. Besides, total oxidant status (TOS), total antioxidant status (TAS), and OSI were determined. Patients with T2DM have higher risk of cardiometabolic changes compared with the control (P = 0.0001). TAS was lower while TOS and OSI were higher in patients with T2DM, as compared with the healthy controls (P < 0.001). TAS, TOS, and OSI were better in patients with T2DM on metformin plus vildagliptin therapy as compared with metformin monotherapy (P < 0.05). Therefore, this study concluded that metformin plus vildagliptin therapy is more effective than metformin monotherapy in attenuation of OSI in patients with T2DM.
Keywords: Oxidative stress index; total antioxidant status; total oxidant status; type II diabetes mellitus.
Copyright: © 2020 Journal of Advanced Pharmaceutical Technology & Research.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abdul-Hadi M, Naji M, Shams H, Sami O, Al-Kuraishy H, Al-Gareeb A. Erectile dysfunction and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A new twist. Int J Nutr Pharmacol Neurol Dis. 2020;10:43–9.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical