Ceria Nanoparticles Decrease UVA-Induced Fibroblast Death Through Cell Redox Regulation Leading to Cell Survival, Migration and Proliferation
- PMID: 33102462
- PMCID: PMC7546350
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.577557
Ceria Nanoparticles Decrease UVA-Induced Fibroblast Death Through Cell Redox Regulation Leading to Cell Survival, Migration and Proliferation
Abstract
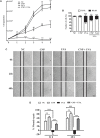
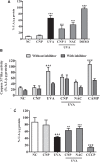
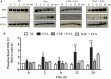
Exposure to ultraviolet radiation is a major contributor to premature skin aging and carcinogenesis, which is mainly driven by overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS). There is growing interest for research on new strategies that address photoaging prevention, such as the use of nanomaterials. Cerium oxide nanoparticles (nanoceria) show enzyme-like activity in scavenging ROS. Herein, our goal was to study whether under ultraviolet A rays (UVA)-induced oxidative redox imbalance, a low dose of nanoceria induces protective effects on cell survival, migration, and proliferation. Fibroblasts cells (L929) were pretreated with nanoceria (100 nM) and exposed to UVA radiation. Pretreatment of cells with nanoceria showed negligible cytotoxicity and protected cells from UVA-induced death. Nanoceria also inhibited ROS production immediately after irradiation and for up to 48 h and restored the superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity and GSH level. Additionally, the nanoceria pretreatment prevented apoptosis by decreasing Caspase 3/7 levels and the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential. Nanoceria significantly improved the cell survival migration and increased proliferation, over a 5 days period, as compared with UVA-irradiated cells, in wound healing assay. Furthermore, it was observed that nanoceria decreased cellular aging and ERK 1/2 phosphorylation. Our study suggests that nanoceria might be a potential ally to endogenous, antioxidant enzymes, and enhancing the redox potentials to fight against UVA-induced photodamage and consequently modulating the cells survival, migration, and proliferation.
Keywords: antioxidant; nanoceria; photoaging; ultraviolet radiation; wound healing.
Copyright © 2020 Ribeiro, de Oliveira, Singh, Sakthivel, Neal, Seal, Ueda-Nakamura, Lautenschlager and Nakamura.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

