COVID-19 in Human, Animal, and Environment: A Review
- PMID: 33102545
- PMCID: PMC7498845
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00578
COVID-19 in Human, Animal, and Environment: A Review
Abstract
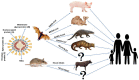
The medical authority in China, especially in Wuhan city, reported on December 2019 a large number of highly fatal, rapidly spreading viral pneumonia caused by an unknown coronavirus. The common history of all the patients was their visiting a Wuhan's whole food store, where live animals and seafood are sold. Irrespective of the efforts of the Chinese authorities, the virus spread rapidly all over the world by travelers, provoking widespread attention by the media and panic. Many previous coronavirus epidemics had been recorded, such as severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS), and the recently newly discovered epidemic is named coronavirus disease of 2019 (COVID-19). This disease is caused by SARS Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), and this virus is antigenically related to the SARS virus (SARS-CoV), which had been detected in 2002, depending on clinical, serological, and molecular findings. There is rapid competition among the researchers to discover the source of the virus, understand the mechanism of the disease development, establish treatment strategies, and determine the factors affecting the incidence of infection and severity of the disease, and focus on the production of a vaccine. Coronaviruses are a group of single-stranded, positive-sense RNA genome viruses; its genome length varies from 26 to 32 kb. Coronavirus causes mild to severe respiratory disorders. In December 2019, several cases of pneumonia of unknown causes were found in Wuhan city, which is located in the Hubei province in China. Chinese health authorities investigated the problem and found that a new virus caused such infection and, using next-generation sequencing, found the 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). It has been transferred from humans to humans and animals to humans (zoonotic). Coronaviruses cause multiple respiratory problems, varying from common cold to severe infections such as SARS. General symptoms of infection include fatigue, cough, and breathing problems such as shortness of breath, as described by World Health Organization. Serious cases may result in pneumonia, renal failure, and even death. We address current information about the new SARS Coronavirus-2 as well as the COVID-19 disease caused by it in this review.
Keywords: COVID-19; animals; clinical studies; environment; epidemiology; human.
Copyright © 2020 Swelum, Shafi, Albaqami, El-Saadony, Elsify, Abdo, Taha, Abdel-Moneim, Al-Gabri, Almaiman, Saleh Al-wajeeh, Tufarelli, Staffa and Abd El-Hack.
Figures
References
-
- Syed A. Coronavirus: a mini-review. Int J Curr Res Med Sci. (2020) 6:8–10.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous