Tilianin Protects against Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Myocardial Injury through the Inhibition of the Ca2+/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase II-Dependent Apoptotic and Inflammatory Signaling Pathways
- PMID: 33102583
- PMCID: PMC7568786
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/5939715
Tilianin Protects against Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Myocardial Injury through the Inhibition of the Ca2+/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase II-Dependent Apoptotic and Inflammatory Signaling Pathways
Abstract
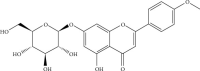
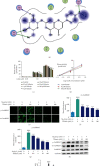
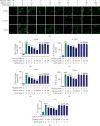
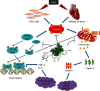
Tilianin is a naturally occurring phenolic compound with a cardioprotective effect against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury (MIRI). The aim of our study was to determine the potential targets and mechanism of action of tilianin against cardiac injury induced by MIRI. An in silico docking model was used in this study for binding mode analysis between tilianin and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII). Oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion- (OGD/R-) injured H9c2 cardiomyocytes and ischemia/reperfusion- (I/R-) injured isolated rat hearts were developed as in vitro and ex vivo models, respectively, which were both treated with tilianin in the absence or presence of a specific CaMKII inhibitor KN93 for target verification and mechanistic exploration. Results demonstrated the ability of tilianin to facilitater the recovery of OGD/R-induced cardiomyocyte injury and the maintenance of cardiac function in I/R-injured hearts. Tilianin interacted with CaMKIIδ with an efficient binding performance, a favorable binding score, and restraining p-CaMKII and ox-CaMKII expression in cardiomyocytes injured by MIRI. Importantly, inhibition of CaMKII abolished tilianin-mediated recovery of OGD/R-induced cardiomyocyte injury and maintenance of cardiac function in I/R-injured hearts, accompanied by the disability to protect mitochondrial function. Furthermore, the protective effects of tilianin towards mitochondrion-associated proapoptotic and antiapoptotic protein counterbalance and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)/nuclear factor- (NF-) κB-related inflammation suppression were both abolished after pharmacological inhibition of CaMKII. Our investigation indicated that the inhibition of CaMKII-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis and JNK/NF-κB inflammation might be considered as a pivotal mechanism used by tilianin to exert its protective effects on MIRI cardiac damage.
Copyright © 2020 Hailun Jiang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Tilianin mediates neuroprotection against ischemic injury by attenuating CaMKII-dependent mitochondrion-mediated apoptosis and MAPK/NF-κB signaling.Life Sci. 2019 Jan 1;216:233-245. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.11.035. Epub 2018 Nov 22. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30472297
-
Tilianin Ameliorates Cognitive Dysfunction and Neuronal Damage in Rats with Vascular Dementia via p-CaMKII/ERK/CREB and ox-CaMKII-Dependent MAPK/NF-κB Pathways.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Sep 4;2021:6673967. doi: 10.1155/2021/6673967. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34527176 Free PMC article.
-
Cardioprotection of tilianin ameliorates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: Role of the apoptotic signaling pathway.PLoS One. 2018 Mar 14;13(3):e0193845. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0193845. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29538428 Free PMC article.
-
CaMKII, 'jack of all trades' in inflammation during cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2023 Nov;184:48-60. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2023.10.003. Epub 2023 Oct 7. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37813179 Review.
-
The Role of NF-κB in Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2022;23(8):535-547. doi: 10.2174/1389203723666220817085941. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2022. PMID: 35980051 Review.
Cited by
-
Adipose Tissue Macrophage Polarization in Healthy and Unhealthy Obesity.Front Nutr. 2021 Feb 17;8:625331. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.625331. eCollection 2021. Front Nutr. 2021. PMID: 33681276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CaMK II in Cardiovascular Diseases, Especially CaMK II-δ: Friends or Enemies.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Aug 5;18:3461-3476. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S473251. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 39132626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective Effects of Flavonoids Against Mitochondriopathies and Associated Pathologies: Focus on the Predictive Approach and Personalized Prevention.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 11;22(16):8649. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168649. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of miRNA and Their Regulatory Effects Induced by Total Flavonoids From Dracocephalum moldavica in the Treatment of Vascular Dementia.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Dec 6;12:796628. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.796628. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34938197 Free PMC article.
-
Tilianin suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activation in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via inhibition of TLR4/NF-κB and NEK7/NLRP3.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Oct 23;15:1423053. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1423053. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39508038 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Backs J., Backs T., Neef S., et al. The delta isoform of CaM kinase II is required for pathological cardiac hypertrophy and remodeling after pressure overload. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2009;106(7):2342–2347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0813013106. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

