Vitamin C as a Supplementary Therapy in Relieving Symptoms of the Common Cold: A Meta-Analysis of 10 Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 33102597
- PMCID: PMC7569434
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/8573742
Vitamin C as a Supplementary Therapy in Relieving Symptoms of the Common Cold: A Meta-Analysis of 10 Randomized Controlled Trials
Erratum in
-
Erratum to "Vitamin C as a Supplementary Therapy in Relieving Symptoms of the Common Cold: A Meta-Analysis of 10 Randomized Controlled Trials".Biomed Res Int. 2021 Apr 27;2021:9875417. doi: 10.1155/2021/9875417. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33997048 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Aim: To investigate whether vitamin C performs well as a supplemental treatment for common cold.
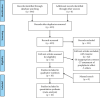
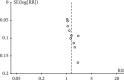
Method: After systematically searching through the National Library of Medicine (PubMed), Cochrane Library, Elsevier, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), VIP databases, and Wanfang databases, 10 randomized controlled trials were selected for our meta-analysis with RevMan 5.3 software. Published in China, all 10 studies evaluated the effect of combined vitamin C and antiviral therapy for the treatment of common cold.
Results: The total efficacy (RR = 1.27, 95% CI (1.08, 1.48), P = 0.003), the time for symptom amelioration (MD = -15.84, 95% CI (-17.02, -14.66), P < 0.00001), and the time for healing (I, 95% CI (-14.98, -4.22), P = 0.0005) were better with vitamin C supplementation than with antiviral therapy alone.
Conclusions: Vitamin C could be used as a supplementary therapy along with antiviral regimens to relieve patients from the symptoms of common cold.
Copyright © 2020 Li Ran et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures

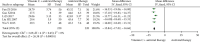
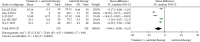
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

