Effects of Arteriovenous Thrombolysis Combined with Mechanical Thrombectomy on Efficacy and Neurological Function of Acute Cerebral Infarct Patients
- PMID: 33102600
- PMCID: PMC7568809
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/9743075
Effects of Arteriovenous Thrombolysis Combined with Mechanical Thrombectomy on Efficacy and Neurological Function of Acute Cerebral Infarct Patients
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Effects of Arteriovenous Thrombolysis Combined with Mechanical Thrombectomy on Efficacy and Neurological Function of Acute Cerebral Infarct Patients.Biomed Res Int. 2024 Mar 20;2024:9872826. doi: 10.1155/2024/9872826. eCollection 2024. Biomed Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38549998 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effects of arteriovenous thrombolysis combined with mechanical thrombectomy on clinical efficacy, neurological function, and the changes of nerve injury markers of acute cerebral infarct (ACI) patients.
Methods: A total of 143 cases with ACI admitted to our hospital from June 2017 to June 2019 were elected as research subjects. Among them, 69 cases of patients who received treatment of arteriovenous thrombolysis were considered as group A, and 74 cases of patients who received treatment of arteriovenous thrombolysis combined with mechanical thrombectomy were considered as group B. NIHSS score, clinical efficacy, vascular recanalization, adverse reactions, hemodynamics, neurological injury indexes, duration of coma, length of hospital stay, and prognosis of patients in the two groups were compared.
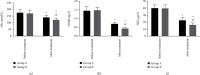
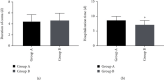
Results: After treatment, the NIHSS score of group A was higher than that of group B (P < 0.05), the clinical efficacy of group B was better than that of group A, and the incidence of adverse reactions was lower than that of group A (P < 0.05). There was no difference in vascular recanalization rate, duration of coma, and prognosis between the two groups (P > 0.05). Length of hospital stay, maximum peak velocity after treatment (Vs), and mean flow rate (Vm) of group A were lower than those of group B, while vascular resistance index (RI), pulsatility index (PI), serum glutamic acid (Glu), neuron-specific enolase (NES), and S100β protein detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) of group A were higher than those of group B (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Arteriovenous thrombolysis combined with mechanical thrombectomy has a significant effect on ACI, with high safety and quick effect. In addition, it has a stronger effect on improving and protecting the neurological function of patients, which is worth promoting in clinical practice.
Copyright © 2020 Tao Ding et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of Standardized Perioperative Management on EEG Indexes and Nerve and Limb Functions of Patients with Acute Cerebral Infarction Undergoing Mechanical Thrombectomy.Dis Markers. 2022 Sep 26;2022:1686891. doi: 10.1155/2022/1686891. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 36199820 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical Thrombectomy for Treatment of Acute Cerebral Infarction due to Distal Medium Vessel Occlusions: A Retrospective Cohort Study.Brain Behav. 2024 Nov;14(11):e70119. doi: 10.1002/brb3.70119. Brain Behav. 2024. PMID: 39508459 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical treatment efficiency of mechanical thrombectomy combined with rhPro-UK thrombolysis for acute moderate/severe cerebral infarction.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Sep;22(17):5740-5746. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201809_15842. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30229852 Clinical Trial.
-
Intra-arterial treatment of patients with acute ischemic stroke and internal carotid artery occlusion: a literature review.J Neurointerv Surg. 2015 Jan;7(1):8-15. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2013-011004. Epub 2014 Jan 2. J Neurointerv Surg. 2015. PMID: 24385555 Review.
-
Comparative efficacy and safety of bridging strategies with direct mechanical thrombectomy in large vessel occlusion: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Apr;98(14):e14956. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014956. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 30946319 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Retracted: Effects of Arteriovenous Thrombolysis Combined with Mechanical Thrombectomy on Efficacy and Neurological Function of Acute Cerebral Infarct Patients.Biomed Res Int. 2024 Mar 20;2024:9872826. doi: 10.1155/2024/9872826. eCollection 2024. Biomed Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38549998 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of intravenous thrombolysis combined with mechanical thrombectomy on neurological function and short-term prognosis of patients with acute cerebral infarction.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Apr 15;14(4):2376-2382. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 35559387 Free PMC article.
-
Sanhua Tang protects against ischemic stroke by preventing blood-brain barrier injury: a network pharmacology and experiments.J Tradit Chin Med. 2024 Aug;44(4):794-803. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240515.001. J Tradit Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 39066540 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of butylphthalide on serum CRP, PARK7, NT-3 and neurological function in patients with acute cerebral infarction.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Sep 15;13(9):10388-10395. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34650707 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

