Mental Fatigue Might Be Not So Bad for Exercise Performance After All: A Systematic Review and Bias-Sensitive Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 33103052
- PMCID: PMC7546119
- DOI: 10.5334/joc.126
Mental Fatigue Might Be Not So Bad for Exercise Performance After All: A Systematic Review and Bias-Sensitive Meta-Analysis
Erratum in
-
Correction: Mental Fatigue Might be Not So Bad for Exercise Performance After All: A Systematic Review and Bias-Sensitive Meta-Analysis.J Cogn. 2021 Jul 19;4(1):32. doi: 10.5334/joc.178. eCollection 2021. J Cogn. 2021. PMID: 34327303 Free PMC article.
Abstract
There is an ongoing debate in the scientific community regarding whether a state of mental fatigue may have a negative effect upon a range of objective and subjective measures of human performance. This issue has attracted attention from several fields, including sport and exercise sciences. In fact, a considerable body of literature in the sport science field has suggested that performing a long and demanding cognitive task might lead to a state of mental fatigue, impairing subsequent exercise performance, although research in this field has shown contradictory results. Here, we performed a meta-analysis to investigate these inconsistent findings. The analysis yielded small-to-medium effects of mental fatigue on exercise performance, d z = 0.50, and RPE, d z = 0.21. However, a three-parameter selection model also revealed evidence of publication or reporting biases, suggesting that the bias-corrected estimates might be substantially lower (0.08 and 0.10, respectively) and non-significant. In sum, current evidence does not provide conclusive support for the claim that mental fatigue has a negative influence on exercise performance.
Keywords: Cognitive Control; Executive functions; Statistical analysis; mental effort.
Copyright: © 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures
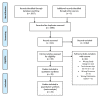

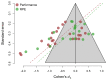
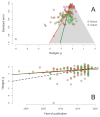
References
-
- Audiffren, M., & André, N. (2015). The strength model of self-control revisited: Linking acute and chronic effects of exercise on executive functions. Journal of Sport and Health Science, 4(1), 30–46. DOI: 10.1016/j.jshs.2014.09.002 - DOI
-
- Becker, J. (2005). Failsafe N or File-Drawer Number In Rothstein H., Sutton M. & Borenstein M. (Eds.), Publication Bias in Meta-Analysis: Prevention, Assessment and Adjustments. Wiley; Retrieved from https://www.wiley.com/en-es/Publication+Bias+in+Meta+Analysis%3A+Prevent... DOI: 10.1002/0470870168.ch7 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

