Growth arrest-specific 2 protein family: Structure and function
- PMID: 33103301
- PMCID: PMC7791176
- DOI: 10.1111/cpr.12934
Growth arrest-specific 2 protein family: Structure and function
Abstract
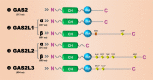
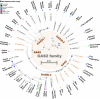
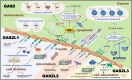
Members of the growth arrest-specific 2 (GAS2) protein family consist of a putative actin-binding (CH) domain and a microtubule-binding (GAR) domain and are considered miniversions of spectraplakins. There are four members in the GAS2 family, viz. GAS2, GAS2L1, GAS2L2 and GAS2L3. Although GAS2 is defined as a family of growth arrest-specific proteins, the significant differences in the expression patterns, interaction characteristics and biological issues or diseases among the different GAS2 family members have not been systemically reviewed to date. Therefore, we summarized the available evidence on the structures and functions of GAS2 family members. This review facilitates a comprehensive molecular understanding of the involvement of the GAS2 family members in an array of biological processes, including cytoskeleton reorganization, cell cycle, apoptosis and cancer development.
Keywords: GAS2; GAS2L1; GAS2L2; GAS2L3; cell cycle; cytoskeleton.
© 2020 The Authors. Cell Proliferation Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Dogterom M, Koenderink GH. Actin‐microtubule crosstalk in cell biology. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20(1):38‐54. - PubMed
-
- Li R, Gundersen GG. Beyond polymer polarity: how the cytoskeleton builds a polarized cell. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9(11):860‐873. - PubMed
-
- Jefferson JJ, Leung CL, Liem RK. Plakins: goliaths that link cell junctions and the cytoskeleton. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5(7):542‐553. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

