Microbiota profile and efficacy of probiotic supplementation on laxation in adults affected by Prader-Willi Syndrome: A randomized, double-blind, crossover trial
- PMID: 33103385
- PMCID: PMC7767560
- DOI: 10.1002/mgg3.1535
Microbiota profile and efficacy of probiotic supplementation on laxation in adults affected by Prader-Willi Syndrome: A randomized, double-blind, crossover trial
Abstract
Background: Probiotics may provide a benefit for adults with Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) experiencing constipation. The primary aim was to determine if Bifidobacterium animalis ssp. lactis B94 (B. lactis B94) improves stool frequency, with secondary aims of stool form and gastrointestinal symptoms. Exploratory aims included diet quality and fecal microbiota composition.
Methods: Following a 4-week baseline, 25 adults with PWS were randomized to consume B. lactis B94 by capsule (15 billion) or placebo for 4 weeks, followed by 4-week washout in a double-blind, crossover design. Stool frequency and Bristol Stool Form (BSF) were assessed daily, and Gastrointestinal Symptom Rating Scale (GSRS) and dietary intake (7-days food records), per period. Fecal microbiota per period was analyzed using 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing and taxa of interest by qPCR (n = 24).
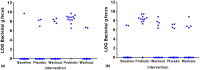
Results: No adverse events were reported. Stool frequency at baseline (n = 25; 2.0 ± 0.1 stools/day), GSRS syndromes, and microbiota composition did not differ with the probiotic intervention overall; however, a delayed, carry-over effect on BSF types 6 and 7 was seen. Diet quality by HEI-2015 was 65.4 ± 8.5.
Conclusion: In adults with PWS, B. lactis B94 exhibited little effect on laxation over 4 weeks; however, further research is needed.
Keywords: Bristol Stool Form; HEI-2015; Prader-Willi syndrome; constipation; probiotic; stool frequency.
© 2020 The Authors. Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures



References
-
- Alyousif, Z. , Miller, J. L. , Sandoval, M. Y. , MacPherson, C. W. , Nagulesapillai, V. , & Dahl, W. J. (2018). The effects of Bifidobacterium animalis ssp. lactis B94 on gastrointestinal wellness in adults with Prader‐Willi syndrome: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials, 19(1), 256. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amir, A. , McDonald, D. , Navas‐Molina, J. A. , Kopylova, E. , Morton, J. T. , Zech Xu, Z. , Kightley, E. P. , Thompson, L. R. , Hyde, E. R. , Gonzalez, A. , & Knight, R. (2017). Deblur rapidly resolves single‐nucleotide community sequence patterns. mSystems, 2(2), e00191‐16 10.1128/mSystems.00191-16 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barichella, M. , Pacchetti, C. , Bolliri, C. , Cassani, E. , Iorio, L. , Pusani, C. , Pinelli, G. , Privitera, G. , Cesari, I. , Faierman, S. A. , Caccialanza, R. , Pezzoli, G. , & Cereda, E. (2016). Probiotics and prebiotic fiber for constipation associated with Parkinson disease: An RCT. Neurology, 87(12), 1274‐1280. 10.1212/wnl.0000000000003127 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

