Combined small cell lung carcinoma harboring ALK rearrangement: A case report and literature review
- PMID: 33103386
- PMCID: PMC7705627
- DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.13716
Combined small cell lung carcinoma harboring ALK rearrangement: A case report and literature review
Abstract
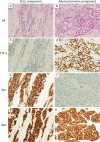
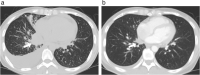
Combined small cell lung cancer (c-SCLC) is a relatively rare subtype of SCLC and is defined by the combination of SCLC and any elements of non-small cell carcinoma (NSCLC). Standard chemotherapy for patients with c-SCLC has not yet been established. Gene mutations such as epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations may be detected in patients with c-SCLC. However, little is known about anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) rearrangement in c-SCLC patients. Here, we report a young female patient who was successfully treated with alectinib for ALK-positive c-SCLC after failure of immunochemotherapy for SCLC and cytotoxic chemotherapy for adenocarcinoma. Moreover, we performed a literature review of EGFR- or ALK-positive c-SCLC patients. Our report suggests that ALK testing may be justified in patients with SCLC that contain an adenocarcinoma component. KEY POINTS: SIGNIFICANT FINDINGS OF THE STUDY: • This is the first report describing the treatment course comprising immunochemotherapy and ALK-TKI in a patient with c-SCLC harboring ALK rearrangement. WHAT THIS STUDY ADDS: • Our case and literature review suggest that although ALK mutation is rare in patients with c-SCLC, its identification and treatment with ALK-TKIs may contribute to clinical benefits.
Keywords: ALK; Alectinib; combined small cell carcinoma; immunochemotherapy; literature review.
© 2020 The Authors. Thoracic Cancer published by China Lung Oncology Group and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transformation of NSCLC to SCLC harboring EML4-ALK fusion with V1180L mutation after alectinib resistance and response to lorlatinib: A case report and literature review.Lung Cancer. 2023 Dec;186:107415. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2023.107415. Epub 2023 Oct 28. Lung Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37907052 Review.
-
PLEKHM2-ALK: A novel fusion in small-cell lung cancer and durable response to ALK inhibitors.Lung Cancer. 2020 Jan;139:146-150. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.11.002. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Lung Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31794921
-
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase expression in small-cell lung cancer.Histopathology. 2019 Jul;75(1):20-28. doi: 10.1111/his.13842. Epub 2019 May 23. Histopathology. 2019. PMID: 30790327
-
ALK-EML4 Fusion in Small Cell Lung Cancer: Clinical and Molecular Insights From a Rare Case.Lung Cancer. 2025 Apr;202:108497. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2025.108497. Epub 2025 Mar 15. Lung Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40106998
-
Small cell lung cancer with EML4-ALK fusion: report of a case responding to ALK TKI and literature review.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2025 Feb 6;151(2):62. doi: 10.1007/s00432-025-06091-3. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39909915 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sustained Clinical Response to 4th-Line Therapy with Selpercatinib in RET Fusion-Positive Combined Small Cell Lung Cancer.Onco Targets Ther. 2023 Nov 29;16:1015-1020. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S440610. eCollection 2023. Onco Targets Ther. 2023. PMID: 38050583 Free PMC article.
-
Combined small cell lung cancer: current progress and unmet needs.Am J Cancer Res. 2023 Sep 15;13(9):3864-3874. eCollection 2023. Am J Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37818075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Successful Treatment of an Elderly Patient With Combined Small Cell Lung Cancer Receiving Anlotinib: A Case Report.Front Oncol. 2021 Nov 11;11:775201. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.775201. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34858856 Free PMC article.
-
A Recurrent Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Harboring an EML4-ALK Fusion Mutation with Sustained Response to Ensartinib: A Case Report.Curr Oncol. 2025 Mar 13;32(3):163. doi: 10.3390/curroncol32030163. Curr Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40136367 Free PMC article.
-
Baseline retinoblastoma transcriptional corepressor 1 (Rb1) functional inactivation is a pre-requisite but not sufficient for small-cell histological transformation in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutant lung adenocarcinomas post-tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy.Virchows Arch. 2025 Feb 21. doi: 10.1007/s00428-025-04054-0. Online ahead of print. Virchows Arch. 2025. PMID: 39982521
References
-
- Travis WD, Brambilla E, Burke AP, Marx A, Nicholson AG. WHO classification of tumours of the lung, pleura, thymus and heart. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer. 2015. - PubMed
-
- Tatematsu A, Shimizu J, Murakami Y et al Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2008; 14: 6092–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

