Why All the Fuss about Oxidative Phosphorylation (OXPHOS)?
- PMID: 33103432
- PMCID: PMC9298160
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01013
Why All the Fuss about Oxidative Phosphorylation (OXPHOS)?
Abstract
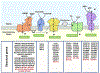
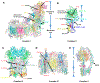
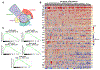
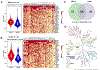
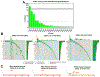
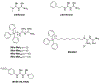
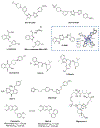
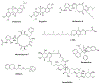
Certain subtypes of cancer cells require oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) to survive. Increased OXPHOS dependency is frequently a hallmark of cancer stem cells and cells resistant to chemotherapy and targeted therapies. Suppressing the OXPHOS function might also influence the tumor microenvironment by alleviating hypoxia and improving the antitumor immune response. Thus, targeting OXPHOS is a promising strategy to treat various cancers. A growing arsenal of therapeutic agents is under development to inhibit this biological process. This Perspective provides an overview of the structure and function of OXPHOS complexes, their biological functions in cancer, relevant research tools and models, as well as the limitations of OXPHOS as drug targets. We also focus on the current development status of OXPHOS inhibitors and potential therapeutic strategies to strengthen their clinical applications.
Figures



References
-
- Roesch A; Vultur A; Bogeski I; Wang H; Zimmermann KM; Speicher D; Korbel C; Laschke MW; Gimotty PA; Philipp SE; Krause E; Patzold S; Villanueva J; Krepler C; Fukunaga-Kalabis M; Hoth M; Bastian BC; Vogt T; Herlyn M Overcoming intrinsic multidrug resistance in melanoma by blocking the mitochondrial respiratory chain of slow-cycling JARID1B(high) cells. Cancer Cell 2013, 23, 811–825. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sriskanthadevan S; Jeyaraju DV; Chung TE; Prabha S; Xu W; Skrtic M; Jhas B; Hurren R; Gronda M; Wang XM; Jitkova Y; Sukhai MA; Lin FH; Maclean N; Laister R; Goard CA; Mullen PJ; Xie S; Penn LZ; Rogers IM; Dick JE; Minden MD; Schimmer AD AML cells have low spare reserve capacity in their respiratory chain that renders them susceptible to oxidative metabolic stress. Blood 2015, 125, 2120–2130. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

