Activation of carbonic anhydrases from human brain by amino alcohol oxime ethers: towards human carbonic anhydrase VII selective activators
- PMID: 33103482
- PMCID: PMC7594847
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2020.1838501
Activation of carbonic anhydrases from human brain by amino alcohol oxime ethers: towards human carbonic anhydrase VII selective activators
Abstract
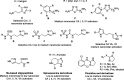
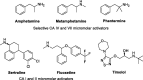
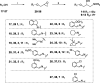
The synthesis and carbonic anhydrase (CA; EC 4.2.1.1) activating effects of a series of oxime ether-based amino alcohols towards four human (h) CA isoforms expressed in human brain, hCA I, II, IV and VII, are described. Most investigated amino alcohol derivatives induced a consistent activation of the tested CAs, with KAs spanning from a low micromolar to a medium nanomolar range. Specifically, hCA II and VII, putative main CA targets when central nervous system (CNS) diseases are concerned, were most efficiently activated by these oxime ether derivatives. Furthermore, a multitude of selective hCA VII activators were identified. As hCA VII is one of the key isoforms involved in brain metabolism and other brain functions, the identified potent and selective hCA VII activators may be considered of interest for investigations of various therapeutic applications or as lead compounds in search of even more potent and selective CA activators.
Keywords: CNS-disease; Metalloenzyme; activation; cognition; selectivity.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures



References
-
- Supuran CT. Carbonic anhydrase activators. Future Med Chem 2018;10:561–73. - PubMed
-
- Main RE, Locke A.. Activation of carbonic anhydrase by histamine. J Biol Chem 1941;140:LXXXI.
-
- Tu CK, Silverman DN, Forsman C, et al. Role of histidine 64 in the catalytic mechanism of human carbonic anhydrase II studied with a site-specific mutant. Biochemistry 1989;28:7913–18. - PubMed
-
- Supuran CT. Carbonic anhydrase activators. Part 4. A general mechanism of action for activators of isozymes I, II and III. Rev Roum Chim 1992;37:411–21.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
