FTO demethylates m6A modifications in HOXB13 mRNA and promotes endometrial cancer metastasis by activating the WNT signalling pathway
- PMID: 33103587
- PMCID: PMC8354663
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1841458
FTO demethylates m6A modifications in HOXB13 mRNA and promotes endometrial cancer metastasis by activating the WNT signalling pathway
Abstract
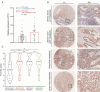
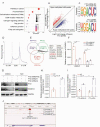
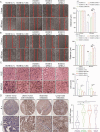
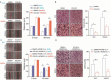
Although many studies have confirmed the relationship between obesity and endometrial cancer (EC), the molecular mechanism between obesity and EC progression has not been elucidated. Overexpression of fat mass and the obesity associated protein FTO leads to weight gain, although recently it has been discovered that FTO can serve as a demethylase which erases N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification and regulates the metabolization of mRNAs. In this study, we found high expression of FTO in metastatic EC and that this action promote both metastasis and invasion in vivo and in vitro. Mechanistically, FTO can catalyse demethylation modification in 3'UTR region of HOXB13 mRNA, thereby abolishing m6A modification recognition with the YTHDF2 protein. Decreasing HOXB13 mRNA decay and increasing HOXB13 protein expression was accompanied by WNT signalling pathway activation and the expression of downstream proteins, leading to tumour metastasis and invasion. We also found the WNT signalling pathway inhibitor ICG-001 can block HOXB13 gene-induced tumour metastasis, therefore ICG-001 may be a promising molecular intervention. This study provides insight into the relationship between obesity and the pathogenesis of endometrial cancer while highlighting future areas of research.
Keywords: Endometrial cancer; cancer metastasis; fto; hoxb13; m6A.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests
Figures



Similar articles
-
RNA N6-methyladenosine demethylase FTO promotes breast tumor progression through inhibiting BNIP3.Mol Cancer. 2019 Mar 28;18(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1004-4. Mol Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30922314 Free PMC article.
-
A novel mechanism of FTO modulating the progression of endometriosis through mediating the m6A methylation of GEF-H1 in a YTHDF1-dependent manner.Mol Med. 2025 Feb 25;31(1):78. doi: 10.1186/s10020-025-01130-8. Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40000966 Free PMC article.
-
FTO/IGF2BP2-mediated N6 methyladenosine modification in invasion and metastasis of thyroid carcinoma via CDH12.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Oct 8;15(10):733. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-07097-4. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 39379360 Free PMC article.
-
FTO m6A Demethylase in Obesity and Cancer: Implications and Underlying Molecular Mechanisms.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 30;23(7):3800. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073800. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Roles of FTO in Neuropsychiatric Disorders.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Apr 26;2022:2677312. doi: 10.1155/2022/2677312. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35528183 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TMEM41A overexpression correlates with poor prognosis and immune alterations in patients with endometrial carcinoma.PLoS One. 2023 Jul 21;18(7):e0285817. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0285817. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37478120 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA GAS5 regulated by FTO-mediated m6A demethylation promotes autophagic cell death in NSCLC by targeting UPF1/BRD4 axis.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Mar;479(3):553-566. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04748-6. Epub 2023 Apr 29. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 37120495
-
METTL14-mediated m6A modification upregulates HOXB13 expression to activate NF-κB and exacerbate cervical cancer progression.Mol Cell Oncol. 2024 Nov 11;11(1):2423986. doi: 10.1080/23723556.2024.2423986. eCollection 2024. Mol Cell Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39534063 Free PMC article.
-
An m6A-Related lncRNA Signature Predicts the Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 30;13:854851. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.854851. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35431958 Free PMC article.
-
m6A demethylase FTO suppresses pancreatic cancer tumorigenesis by demethylating PJA2 and inhibiting Wnt signaling.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021 Jun 24;25:277-292. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.06.005. eCollection 2021 Sep 3. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021. Retraction in: Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022 May 04;28:536. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2022.04.023. PMID: 34484859 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Katz A.CE: obesity-related cancer in women: a clinical review. Am J Nurs. 2019;119:34–41. - PubMed
-
- Carugno J. Clinical management of vaginal bleeding in postmenopausal women. Climacteric. 2020;23:343–349. - PubMed
-
- Dai Y, Wang Z, Wang J. Survival of microsatellite-stable endometrioid endometrial cancer patients after minimally invasive surgery: an analysis of the cancer genome Atlas data. Gynecol Oncol. 2020;158:92–98. - PubMed
-
- Han C, Altwerger G, Menderes G, et al. Novel targeted therapies in ovarian and uterine carcinosarcomas. Discov Med. 2018;25:309–319. - PubMed
-
- Travaglino A, Raffone A, Stradella C, et al. Impact of endometrial carcinoma histotype on the prognostic value of the TCGA molecular subgroups. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2020;301:1355–1363. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
