Identifying Ethical Considerations for Machine Learning Healthcare Applications
- PMID: 33103967
- PMCID: PMC7737650
- DOI: 10.1080/15265161.2020.1819469
Identifying Ethical Considerations for Machine Learning Healthcare Applications
Abstract
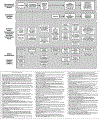
Along with potential benefits to healthcare delivery, machine learning healthcare applications (ML-HCAs) raise a number of ethical concerns. Ethical evaluations of ML-HCAs will need to structure the overall problem of evaluating these technologies, especially for a diverse group of stakeholders. This paper outlines a systematic approach to identifying ML-HCA ethical concerns, starting with a conceptual model of the pipeline of the conception, development, implementation of ML-HCAs, and the parallel pipeline of evaluation and oversight tasks at each stage. Over this model, we layer key questions that raise value-based issues, along with ethical considerations identified in large part by a literature review, but also identifying some ethical considerations that have yet to receive attention. This pipeline model framework will be useful for systematic ethical appraisals of ML-HCA from development through implementation, and for interdisciplinary collaboration of diverse stakeholders that will be required to understand and subsequently manage the ethical implications of ML-HCAs.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; effectiveness; ethics; machine learning; safety; test characteristics.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures:
Danton Char and Chris Feudtner have no financial conflicts of interest to declare.
Michael Abramoff is Founder and Executive Chairman of IDx, and has patents, patent applications, ownership, employment, and consultancy related to the subject of this article.
Figures
Comment in
-
Planning for the Known Unknown: Machine Learning for Human Healthcare Systems.Am J Bioeth. 2020 Nov;20(11):1-3. doi: 10.1080/15265161.2020.1822674. Am J Bioeth. 2020. PMID: 33103968 No abstract available.
-
What Counts as "Clinical Data" in Machine Learning Healthcare Applications?Am J Bioeth. 2020 Nov;20(11):27-30. doi: 10.1080/15265161.2020.1820107. Am J Bioeth. 2020. PMID: 33103969 No abstract available.
-
Deepening the Normative Evaluation of Machine Learning Healthcare Application by Complementing Ethical Considerations with Regulatory Governance.Am J Bioeth. 2020 Nov;20(11):43-45. doi: 10.1080/15265161.2020.1820106. Am J Bioeth. 2020. PMID: 33103970 No abstract available.
-
What's in the Box?: Uncertain Accountability of Machine Learning Applications in Healthcare.Am J Bioeth. 2020 Nov;20(11):37-40. doi: 10.1080/15265161.2020.1820105. Am J Bioeth. 2020. PMID: 33103971 No abstract available.
-
Machine Learning Healthcare Applications (ML-HCAs) Are No Stand-Alone Systems but Part of an Ecosystem - A Broader Ethical and Health Technology Assessment Approach is Needed.Am J Bioeth. 2020 Nov;20(11):46-48. doi: 10.1080/15265161.2020.1820104. Am J Bioeth. 2020. PMID: 33103972 No abstract available.
-
It is Time for Bioethicists to Enter the Arena of Machine Learning Ethics.Am J Bioeth. 2020 Nov;20(11):18-20. doi: 10.1080/15265161.2020.1820115. Am J Bioeth. 2020. PMID: 33103973 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Machine Learning in Healthcare: Exceptional Technologies Require Exceptional Ethics.Am J Bioeth. 2020 Nov;20(11):48-51. doi: 10.1080/15265161.2020.1820103. Am J Bioeth. 2020. PMID: 33103974 No abstract available.
-
Addressing the "Wicked" Problems in Machine Learning Applications - Time for Bioethical Agility.Am J Bioeth. 2020 Nov;20(11):25-27. doi: 10.1080/15265161.2020.1820114. Am J Bioeth. 2020. PMID: 33103975 No abstract available.
-
Structural Disparities in Data Science: A Prolegomenon for the Future of Machine Learning.Am J Bioeth. 2020 Nov;20(11):35-37. doi: 10.1080/15265161.2020.1820102. Am J Bioeth. 2020. PMID: 33103976 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Embedded Ethics Could Help Implement the Pipeline Model Framework for Machine Learning Healthcare Applications.Am J Bioeth. 2020 Nov;20(11):32-35. doi: 10.1080/15265161.2020.1820101. Am J Bioeth. 2020. PMID: 33103978 No abstract available.
-
Keeping the Patient at the Center of Machine Learning in Healthcare.Am J Bioeth. 2020 Nov;20(11):54-56. doi: 10.1080/15265161.2020.1820100. Am J Bioeth. 2020. PMID: 33103979 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Accountability in the Machine Learning Pipeline: The Critical Role of Research Ethics Oversight.Am J Bioeth. 2020 Nov;20(11):40-42. doi: 10.1080/15265161.2020.1820111. Am J Bioeth. 2020. PMID: 33103980 No abstract available.
-
Where Bioethics Meets Machine Ethics.Am J Bioeth. 2020 Nov;20(11):22-24. doi: 10.1080/15265161.2020.1819471. Am J Bioeth. 2020. PMID: 33103981 No abstract available.
-
An Ethical Framework to Nowhere.Am J Bioeth. 2020 Nov;20(11):30-32. doi: 10.1080/15265161.2020.1820109. Am J Bioeth. 2020. PMID: 33103982 No abstract available.
-
AI Ethics Is Not a Panacea.Am J Bioeth. 2020 Nov;20(11):20-22. doi: 10.1080/15265161.2020.1819470. Am J Bioeth. 2020. PMID: 33103983 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Respect and Trustworthiness in the Patient-Provider-Machine Relationship: Applying a Relational Lens to Machine Learning Healthcare Applications.Am J Bioeth. 2020 Nov;20(11):51-53. doi: 10.1080/15265161.2020.1820108. Am J Bioeth. 2020. PMID: 33103984 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A Framework to Evaluate Ethical Considerations with ML-HCA Applications-Valuable, Even Necessary, but Never Comprehensive.Am J Bioeth. 2020 Nov;20(11):W6-W10. doi: 10.1080/15265161.2020.1827695. Am J Bioeth. 2020. PMID: 33103985 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
An Evaluation of the Pipeline Framework for Ethical Considerations in Machine Learning Healthcare Applications: The Case of Prediction from Functional Neuroimaging Data.Am J Bioeth. 2020 Nov;20(11):56-58. doi: 10.1080/15265161.2020.1820110. Am J Bioeth. 2020. PMID: 33103986 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hern Alex. 2017. “Royal Free Breached UK Data Law in 1.6m Patient Deal with Google’s DeepMind.” The Guardian, July 3, 2017 https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2017/jul/03/google-deepmind-16m-p....
-
- Angwin Julia, Larson Jeff, Mattu Surya, and Kirchner Lauren. 2016. “Machine Bias: There’s Software Used across the Country to Predict Future Criminals. And It’s Biased against Blacks.” ProPublica. May 23, 2016 https://www.propublica.org/article/machine-bias-risk-assessments-in-crim....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources