Treating Parkinson's Disease with Antibodies: Previous Studies and Future Directions
- PMID: 33104039
- PMCID: PMC7990466
- DOI: 10.3233/JPD-202221
Treating Parkinson's Disease with Antibodies: Previous Studies and Future Directions
Abstract
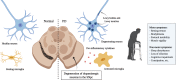
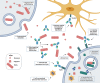
Parkinson's disease is a neurodegenerative disorder mainly characterized by the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra. Degenerating neurons contain abnormal aggregates called Lewy bodies, that are predominantly composed of the misfolded and/or mutated alpha-synuclein protein. Post-translational modifications, cellular stress, inflammation and gene mutations are thought to trigger its pathological misfolding and aggregation. With alpha-synuclein pathology being strongly associated with dopaminergic neuronal toxicity, strategies aimed to reduce its burden are expected to be beneficial in slowing disease progression. Moreover, multiple sources of evidence suggest a cell-to-cell transmission of pathological alpha-synuclein in a prion-like manner. Therefore, antibodies targeting extra- or intracellular alpha-synuclein could be efficient in limiting the aggregation and transmission. Several active and passive immunization strategies have been explored to target alpha-synuclein. Here, we summarize immunotherapeutic approaches that were tested in pre-clinical or clinical studies in the last two decades in an attempt to treat Parkinson's disease.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; alpha-synuclein; antibodies; immunotherapy; intrabodies.; nanobodies; prion-like.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to report.
Figures
References
-
- Gelb DJ, Oliver E, Gilman S (1999) Diagnostic criteria for Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 56, 33–39. - PubMed
-
- Postuma RB, Aarsland D, Barone P, Burn DJ, Hawkes CH, Oertel W, Ziemssen T (2012) Identifying prodromal Parkinson’s disease: Pre-Motor disorders in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 27, 617–626. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

