Hospitalizations for Chronic Disease and Acute Conditions in the Time of COVID-19
- PMID: 33104158
- PMCID: PMC7589070
- DOI: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.3978
Hospitalizations for Chronic Disease and Acute Conditions in the Time of COVID-19
Abstract
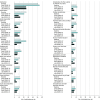
This study examines the frequency of hospitalization for all non–COVID-19-related conditions in a health system at the epicenter of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Deferral of Care for Serious Non-COVID-19 Conditions: A Hidden Harm of COVID-19.JAMA Intern Med. 2021 Feb 1;181(2):274. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.4016. JAMA Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 33104166 No abstract available.
Comment on
-
Factors associated with hospital admission and critical illness among 5279 people with coronavirus disease 2019 in New York City: prospective cohort study.BMJ. 2020 May 22;369:m1966. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m1966. BMJ. 2020. PMID: 32444366 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project Clinical Classifications Software Refined (CCSR) for ICD-10-CM diagnoses. Accessed May 26, 2020. https://www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/toolssoftware/ccsr/ccs_refined.jsp
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical