Prevalence and Characteristics of Telehealth Utilization in the United States
- PMID: 33104208
- PMCID: PMC7588937
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.22302
Prevalence and Characteristics of Telehealth Utilization in the United States
Abstract
Importance: Telehealth services, which allow patients to communicate with a remotely located clinician, are increasingly available; however, prevalence of telehealth use, including videoconferencing visits, remains unclear.
Objective: To measure the use of and willingness to use telehealth modalities across the US population.
Design, setting, and participants: This survey study, conducted between February 2019 and April 2019, asked participants about their use of different telehealth modalities, reasons for not using videoconferencing visits, and willingness to use videoconferencing visits. Questions were continuously posed to panel members and closed after 2555 responses were obtained, at which point 3932 panel members had been invited, for a 65.0% response rate.
Exposures: Demographic characteristics (ie, age, sex, race, rural/urban residency, education level, and income).
Main outcomes and measures: Self-reported use of specific telehealth modalities, reasons for nonuse, and willingness to use videoconferencing in the future.
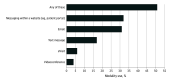
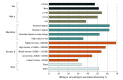
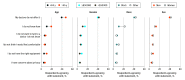
Results: A total of 2555 individuals completed the survey with a mean (SD) age of 57.2 (14.2) years; 1453 respondents (weighted percentage, 51.9%) were women, and 2043 (weighted percentage, 73.4%) were White individuals. Overall, 1343 respondents (weighted percentage, 50.8%) reported use of a nontelephone telehealth modality, ranging from 873 respondents (weighted percentage, 31.9%) for patient portals and 89 respondents (weighted percentage, 4.2%) for videoconferencing visits. Although 1309 respondents (weighted percentage, 49.2%) overall answered that they were willing or very willing to use videoconferencing visits, respondents who were Black individuals (OR, 0.58; 95% CI, 0.38-0.91), aged older than 65 years (OR, 0.51; 95% CI, 0.40-0.66), or had less education (high school or less vs advanced degrees: OR, 0.37; 95% CI, 0.25-0.56) were less likely to express willingness.
Conclusions and relevance: Despite the focused policy attention on videoconferencing visits, the results of this survey study suggest that other forms of telehealth were more dominant prior to 2020. Targeted efforts may be necessary for videoconferencing visits to reach patient groups who are older or have less education, and payer policies supporting other forms of telemedicine may be appropriate to enhance access.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Mims C. Ask not for whom the doorbell tolls. They won’t answer it. Wall Street Journal Published August 28, 2017. Accessed November 9, 2019. https://www.wsj.com/articles/ask-not-for-whom-the-doorbell-tolls-they-wo...
-
- Office of Health Policy, Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation Report to Congress: E-health and telemedicine. Published August 12, 2016. Accessed September 9, 2020. https://aspe.hhs.gov/system/files/pdf/206751/TelemedicineE-HealthReport.pdf
-
- Frist B. Telemedicine: a solution to address the problems of cost, access, and quality. Health Affairs Blog. Published July 23, 2015. Accessed January 27, 2020. https://www.healthaffairs.org/do/10.1377/hblog20150723.049490/full/ - DOI
-
- FAIR Health A multilayered analysis of telehealth: how this emerging venue of care is affecting the healthcare landscape. Published July 2019. Accessed September 9, 2020. https://s3.amazonaws.com/media2.fairhealth.org/whitepaper/asset/A%20Mult...
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

