Perivascular Inflammation in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
- PMID: 33105588
- PMCID: PMC7690279
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9112338
Perivascular Inflammation in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Abstract
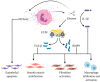
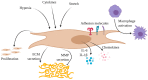
Perivascular inflammation is a prominent pathologic feature in most animal models of pulmonary hypertension (PH) as well as in pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) patients. Accumulating evidence suggests a functional role of perivascular inflammation in the initiation and/or progression of PAH and pulmonary vascular remodeling. High levels of cytokines, chemokines, and inflammatory mediators can be detected in PAH patients and correlate with clinical outcome. Similarly, multiple immune cells, including neutrophils, macrophages, dendritic cells, mast cells, T lymphocytes, and B lymphocytes characteristically accumulate around pulmonary vessels in PAH. Concomitantly, vascular and parenchymal cells including endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, and fibroblasts change their phenotype, resulting in altered sensitivity to inflammatory triggers and their enhanced capacity to stage inflammatory responses themselves, as well as the active secretion of cytokines and chemokines. The growing recognition of the interaction between inflammatory cells, vascular cells, and inflammatory mediators may provide important clues for the development of novel, safe, and effective immunotargeted therapies in PAH.
Keywords: inflammation; pulmonary hypertension; vascular remodeling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cytokines, Chemokines, and Inflammation in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1303:275-303. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-63046-1_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33788198
-
Chronic inflammation within the vascular wall in pulmonary arterial hypertension: more than a spectator.Cardiovasc Res. 2020 Apr 1;116(5):885-893. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvz308. Cardiovasc Res. 2020. PMID: 31813986 Review.
-
Immunity and inflammation in pulmonary arterial hypertension: From pathophysiology mechanisms to treatment perspective.Pharmacol Res. 2022 Jun;180:106238. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106238. Epub 2022 Apr 30. Pharmacol Res. 2022. PMID: 35504356 Review.
-
Pulmonary hypertension: Linking inflammation and pulmonary arterial stiffening.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 5;13:959209. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.959209. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36275740 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunotherapy for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: From the Pathogenesis to Clinical Management.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 1;25(15):8427. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158427. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125996 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of biomarkers related to copper metabolism in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension.BMC Pulm Med. 2023 Jan 23;23(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s12890-023-02326-6. BMC Pulm Med. 2023. PMID: 36690956 Free PMC article.
-
CC chemokines Modulate Immune responses in Pulmonary Hypertension.J Adv Res. 2024 Sep;63:171-186. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2023.10.015. Epub 2023 Nov 4. J Adv Res. 2024. PMID: 37926143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of macrophages in pulmonary arterial hypertension.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 19;14:1152881. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1152881. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37153557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zhishi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction modulates hypoxia and lipid toxicity to alleviate pulmonary vascular remodeling of pulmonary hypertension in rats.Chin Med. 2024 Dec 19;19(1):173. doi: 10.1186/s13020-024-01039-0. Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 39696593 Free PMC article.
-
Essential Roles of PIEZO1 in Mammalian Cardiovascular System: From Development to Diseases.Cells. 2024 Aug 26;13(17):1422. doi: 10.3390/cells13171422. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39272994 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Savai R., Pullamsetti S.S., Kolbe J., Bieniek E., Voswinckel R., Fink L., Scheed A., Ritter C., Dahal B.K., Vater A., et al. Immune and inflammatory cell involvement in the pathology of idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012;186:897–908. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201202-0335OC. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Humbert M., Monti G., Brenot F., Sitbon O., Portier A., Grangeot-Keros L., Duroux P., Galanaud P., Simonneau G., Emilie D. Increased interleukin-1 and interleukin-6 serum concentrations in severe primary pulmonary hypertension. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995;151:1628–1631. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.151.5.7735624. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

