Hereditary Hypofibrinogenemia with Hepatic Storage
- PMID: 33105716
- PMCID: PMC7659954
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21217830
Hereditary Hypofibrinogenemia with Hepatic Storage
Abstract
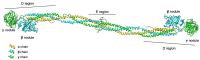
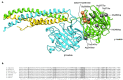
Fibrinogen is a 340-kDa plasma glycoprotein constituted by two sets of symmetrical trimers, each formed by the Aα, Bβ, and γ chains (respectively coded by the FGA, FGB, and FGG genes). Quantitative fibrinogen deficiencies (hypofibrinogenemia, afibrinogenemia) are rare congenital disorders characterized by low or unmeasurable plasma fibrinogen antigen levels. Their genetic basis is represented by mutations within the fibrinogen genes. To date, only eight mutations, all affecting a small region of the fibrinogen γ chain, have been reported to cause hereditary hypofibrinogenemia with hepatic storage (HHHS), a disorder characterized by protein aggregation in the endoplasmic reticulum, hypofibrinogenemia, and liver disease of variable severity. Here, we will briefly review the clinic characteristics of HHHS patients and the histological feature of their hepatic inclusions, and we will focus on the molecular genetic basis of this peculiar type of coagulopathy.
Keywords: FGG gene; fibrinogen; hepatic inclusion; hereditary hypofibrinogenemia with hepatic storage; hypofibrinogenemia; mutation; prevalence; storage disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTex) Database, v8. [(accessed on 3 August 2020)]; Available online: https://www.gtexportal.org/home/
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

