Neutrophilic inflammation during lung development disrupts elastin assembly and predisposes adult mice to COPD
- PMID: 33108351
- PMCID: PMC7773387
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI139481
Neutrophilic inflammation during lung development disrupts elastin assembly and predisposes adult mice to COPD
Abstract
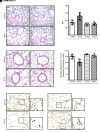
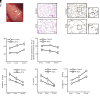
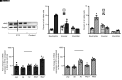
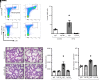
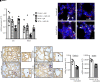
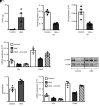
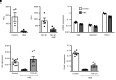
Emerging evidence indicates that early life events can increase the risk for developing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Using an inducible transgenic mouse model for NF-κB activation in the airway epithelium, we found that a brief period of inflammation during the saccular stage (P3-P5) but not alveolar stage (P10-P12) of lung development disrupted elastic fiber assembly, resulting in permanent reduction in lung function and development of a COPD-like lung phenotype that progressed through 24 months of age. Neutrophil depletion prevented disruption of elastic fiber assembly and restored normal lung development. Mechanistic studies uncovered a role for neutrophil elastase (NE) in downregulating expression of critical elastic fiber assembly components, particularly fibulin-5 and elastin. Further, purified human NE and NE-containing exosomes from tracheal aspirates of premature infants with lung inflammation downregulated elastin and fibulin-5 expression by saccular-stage mouse lung fibroblasts. Together, our studies define a critical developmental window for assembling the elastin scaffold in the distal lung, which is required to support lung structure and function throughout the lifespan. Although neutrophils play a well-recognized role in COPD development in adults, neutrophilic inflammation may also contribute to early-life predisposition to COPD.
Keywords: COPD; Extracellular matrix; Inflammation; Neutrophils; Pulmonology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 HL092870/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K12 HD087023/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL130595/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM108807/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK058404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL127102/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL143051/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HL135710/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- L40 HL138848/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA068485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX002378/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01 HL145372/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL141652/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL102371/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HL143281/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY008126/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL094296/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 HL154287/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 CX001969/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- K08 HL133484/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL119503/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- IK2 BX003841/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- U24 DK059637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL153246/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

