Ultra-deformable liposomes containing terpenes (terpesomes) loaded fenticonazole nitrate for treatment of vaginal candidiasis: Box-Behnken design optimization, comparative ex vivo and in vivo studies
- PMID: 33108907
- PMCID: PMC7594706
- DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2020.1837295
Ultra-deformable liposomes containing terpenes (terpesomes) loaded fenticonazole nitrate for treatment of vaginal candidiasis: Box-Behnken design optimization, comparative ex vivo and in vivo studies
Abstract
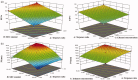
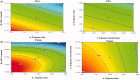
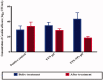
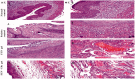
Fenticonazole nitrate (FTN) is a potent antifungal drug adopted in the treatment of vaginal candidiasis. It has inadequate aqueous solubility hence, novel ultra-deformable liposomes 'Terpesomes' (TPs) were developed that might prevail over FTN poor solubility besides TPs might abstain the obstacles of mucus invasion. TPs were assembled by thin-film hydration then optimized by Box Behnken design utilizing terpenes ratio (X1), sodium deoxycholate amount (X2), and ethanol concentration (X3) as independent variable, whereas their impact was inspected for entrapment efficiency (Y1), particle size (Y2), and polydispersity index (Y3). Design Expert® was bestowed to select the optimal TP for more studies. The optimal TP had entrapment efficiency of 62.18 ± 1.39%, particle size of 310.00 ± 8.16 nm, polydispersity index of 0.20 ± 0.10, and zeta potential of -10.19 ± 0.2.00 mV. Elasticity results were greater in the optimal TP related to classical bilosomes. Further, ex vivo permeation illustrated tremendous permeability from the optimal TP correlated to classical bilosomes, and FTN suspension. Besides, in vivo assessment displayed significant inhibition effect in rats from FTN-TPs gel compared to FTN gel. The antifungal potency with undermost histopathological variation was detected in rats treated with FTN-TPs gel. Overall, the acquired findings verified the potency of utilizing FTN-TPs gel for treatment of vaginal candidiasis.
Keywords: Box Behnken design; fenticonazole nitrate; microbiological study; terpesomes; ultra-deformable liposomes; vaginal drug delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Abdelbary AA, AbouGhaly MH. (2015). Design and optimization of topical methotrexate loaded niosomes for enhanced management of psoriasis: application of Box-Behnken design, in-vitro evaluation and in-vivo skin deposition study. Int J Pharm 485:235–43. - PubMed
-
- Abdellatif MM, Khalil IA, Khalil MA. (2017). Sertaconazole nitrate loaded nanovesicular systems for targeting skin fungal infection: In-vitro, ex-vivo and in-vivo evaluation. Int J Pharm 527:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Aboelazayem O, Gadalla M, Saha B. (2018). Valorisation of high acid value waste cooking oil into biodiesel using supercritical methanolysis: Experimental assessment and statistical optimisation on typical Egyptian feedstock. Energy 162:408–20.
-
- Aboud HM, Ali AA, El-Menshawe SF, Elbary AA. (2016). Nanotransfersomes of carvedilol for intranasal delivery: formulation, characterization and in vivo evaluation. Drug Deliv 23:2471–81. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
